Human Nutrition Vocabulary Set in Eating, Drinking and Serving: Full and Detailed List
The 'Human Nutrition' vocabulary set in 'Eating, Drinking and Serving' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /ˌæn.t̬iˈɑːk.sɪ.dənt/
Example:
Vitamins C and E are well-known antioxidants.
/ˌkɑːr.boʊˈhaɪ.dreɪt/
Example:
Pasta is a good source of carbohydrates.
/ˌæm.ɪ.noʊ ˈæs.ɪd/
Example:
Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids.
/ˈproʊ.tiːn/
Example:
Meat, eggs, and beans are good sources of protein.
/ˈfæt.i ˌæs.ɪd/
Example:
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health.
/ˈlɪp.ɪd/
Example:
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a bilayer of lipids.
/nuːˌkliː.ɪk ˈæs.ɪd/
Example:
DNA is a type of nucleic acid that carries genetic information.
/fæt/
Example:
The chef trimmed the excess fat from the meat.
/ˈfaɪ.bɚ/
Example:
Cotton fibers are used to make fabric.
/ˈmɪn.ər.əl/
Example:
Quartz is a common mineral found in many rocks.
/nuːˈtrɪʃ.ən/
Example:
Good nutrition is essential for a healthy life.
/ɪˈsen.ʃəl/
Example:
Water is essential for life.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə-/
Example:
Citrus fruits are rich in vitamin C.
/ˈwɑː.t̬ɚ/
Example:
Please give me a glass of water.
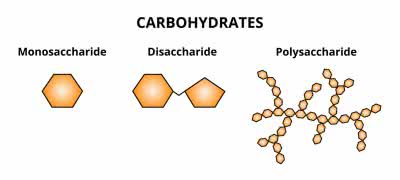
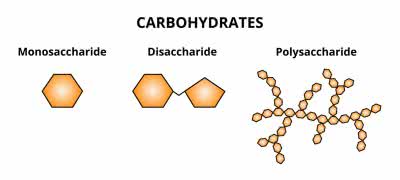
/ˌmɑː.noʊˈsæk.ə.raɪd/
Example:
Glucose is a common monosaccharide found in many foods.
/ˈɡluː.koʊs/
Example:
The body converts carbohydrates into glucose for energy.
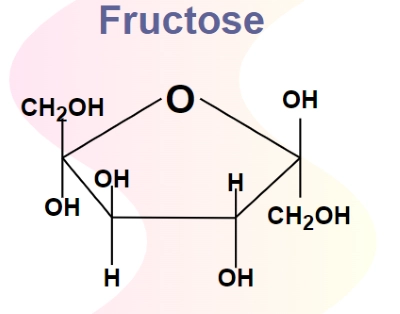
/ˈfrʊk.toʊs/
Example:
Many fruits are rich in fructose.
/ˌpɑː.lɪˈsæk.ər.aɪd/
Example:
Starch is a common polysaccharide found in plants.
/stɑːrtʃ/
Example:
Potatoes are a good source of starch.
/traɪˈɡlɪs.ə.raɪd/
Example:
High levels of triglycerides in the blood can increase the risk of heart disease.
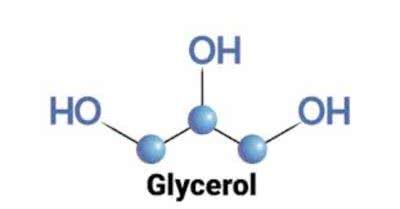
/ˈɡlɪs.ə.rɑːl/
Example:
Glycerol is commonly used in cosmetics for its moisturizing properties.
/daɪˈsæk.ə.raɪd/
Example:
Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk.
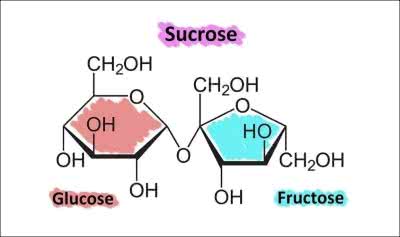
/ˈsuː.kroʊs/
Example:
Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose.
/ˈlæk.toʊs/
Example:
Many adults are unable to digest lactose.
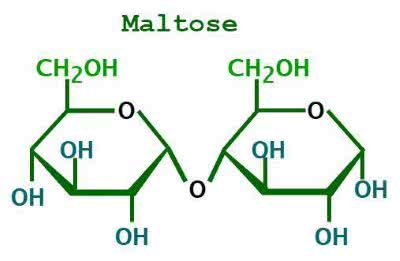
/ˈmɔːl.toʊz/
Example:
Maltose is a sugar produced when starch breaks down.
/ˈɡlaɪ.koʊ.dʒən/
Example:
The liver stores glycogen as a primary energy reserve.
/ˈoʊ.mɪɡ.ə ˈθriː/
Example:
Eating fatty fish like salmon provides a good source of Omega-3.
/træns ˈfæt.i ˈæs.ɪd/
Example:
Many processed foods contain trans fatty acids, which are harmful to heart health.
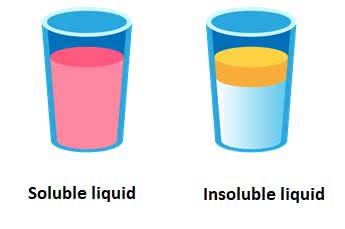
/ɪnˈsɑːl.jə.bəl/
Example:
The problem seemed insoluble.
/ˈsɑːl.jə.bəl/
Example:
Sugar is soluble in water.
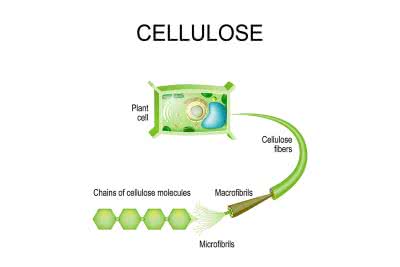
/ˈsel.jə.loʊs/
Example:
Wood is primarily composed of cellulose.
/ˈen.zaɪm/
Example:
Digestion relies on various enzymes to break down food.
/ˈkæl.si.əm/
Example:
Milk is a good source of calcium.
/ˈklɔːr.iːn/
Example:
Swimming pools are often treated with chlorine to kill bacteria.
/mæɡˈniː.zi.əm/
Example:
Magnesium is an essential mineral for human health.
/ˈfɑːs.fɚ.əs/
Example:
Phosphorus is an essential element for all living organisms.
/pəˈtæs.i.əm/
Example:
Bananas are a good source of potassium.
/ˈsoʊ.di.əm/
Example:
Table salt is primarily composed of sodium chloride.
/ˈkɑː.pɚ/
Example:
Electrical wires are often made of copper.
/ˈaɪ.ə.diːn/
Example:
The doctor applied iodine to the wound to prevent infection.
/aɪrn/
Example:
The bridge was built with steel and iron.
/ˈmæŋ.ɡə.niːz/
Example:
Manganese is an essential component in the production of stainless steel.
/mɑːˈlɪb.də.nəm/
Example:
Molybdenum is an essential trace element for plants and animals.
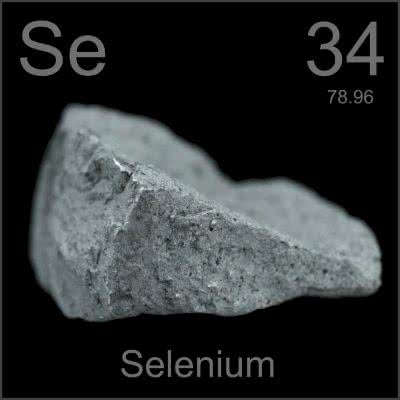
/səˈliː.ni.əm/
Example:
Selenium is an essential trace element for humans, but can be toxic in large amounts.
/zɪŋk/
Example:
Galvanized steel is coated with zinc to prevent rust.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn diː/
Example:
Sunlight helps the body produce vitamin D.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn siː/
Example:
Oranges are a good source of vitamin C.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn eɪ/
Example:
Carrots are a good source of vitamin A.
/ˈvaɪ.tə.mɪn biː wʌn/
Example:
Lack of vitamin B1 can lead to beriberi.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn biː ˈtuː/
Example:
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is essential for energy metabolism.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn biː twelv/
Example:
Many vegans take vitamin B12 supplements because it's primarily found in animal products.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn iː/
Example:
Many skin creams contain vitamin E for its antioxidant properties.
/ˈvaɪ.t̬ə.mɪn keɪ/
Example:
Leafy green vegetables are a good source of vitamin K.
/əˌskɔːr.bɪk ˈæs.ɪd/
Example:
Citrus fruits are rich in ascorbic acid.
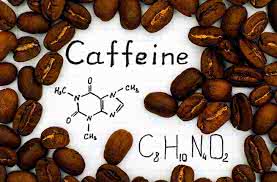
/ˈkæf.iːn/
Example:
Coffee contains a high amount of caffeine.
/ɪˈmʌl.sə.faɪ.ɚ/
Example:
Lecithin is a common emulsifier used in chocolate.
/ˈfoʊ.lɪk ˈæs.ɪd/
Example:
Pregnant women are advised to take folic acid supplements.
/ˈɡluː.t̬ən/
Example:
Many people are choosing to eat foods that are free of gluten.
/ˌmɑː.noʊˌsoʊ.di.əm ˈɡluː.tə.meɪt/
Example:
Many processed foods contain monosodium glutamate to improve taste.
/ˈnaɪə.sɪn/
Example:
Foods rich in niacin include chicken, fish, and peanuts.
/ˌsoʊ.di.əm baɪˈkɑːr.bən.ət/
Example:
Add a teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate to the mixture for leavening.
/ˈtæn.ɪn/
Example:
The strong tea had a high concentration of tannin.
/ˈθaɪ.ə.mɪn/
Example:
Foods rich in thiamin include whole grains, pork, and legumes.