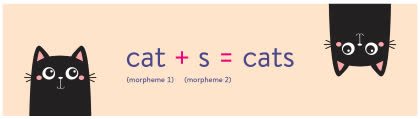Vokabelsammlung Linguistik in Niveau C2: Vollständige und detaillierte Liste
Die Vokabelsammlung 'Linguistik' in 'Niveau C2' wurde sorgfältig aus standardisierten internationalen Lehrbüchern ausgewählt und hilft Ihnen, den Wortschatz in kurzer Zeit zu meistern. Umfassende Definitionen, Beispielsätze und Standardaussprache...
Diese Vokabelsammlung bei Lingoland lernen
Jetzt lernen(noun) Weitschweifigkeit, Redundanz, Ausführlichkeit
Beispiel:
(noun) Rhetorik, Redekunst
Beispiel:
(noun) Beiname, Epitheton, Schimpfwort
Beispiel:
(noun) Intertextualität
Beispiel:
(noun) Apposition, Nebeneinanderstellung, Beisatz
Beispiel:
(noun) Kofferwort
Beispiel:
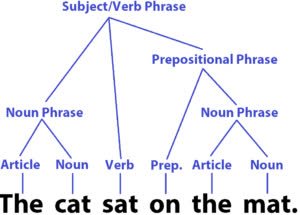
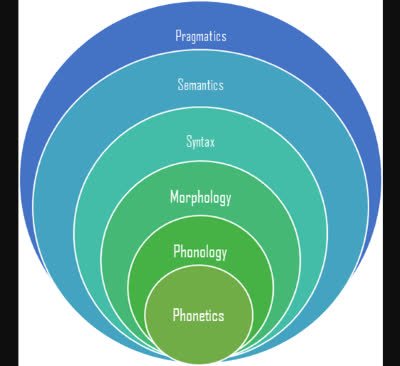
(noun) Syntax, Satzbau
Beispiel:
(noun) Morphem
Beispiel:
(noun) Semantik, Bedeutung, Sinn
Beispiel:
(noun) Lexikon, Wortschatz, Wörterbuch
Beispiel:
(noun) Anapher
Beispiel:
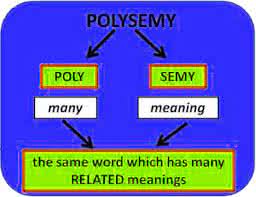
(noun) Polysemie, Mehrdeutigkeit
Beispiel:
(noun) Allophon
Beispiel:
(noun) Lexem
Beispiel:
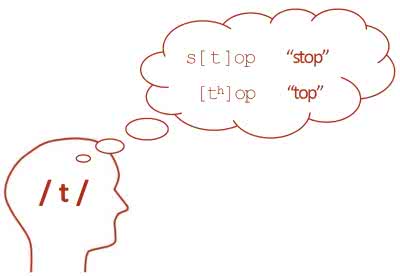
(noun) Phonem
Beispiel:
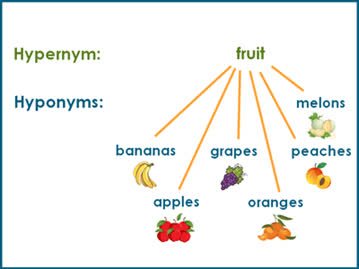
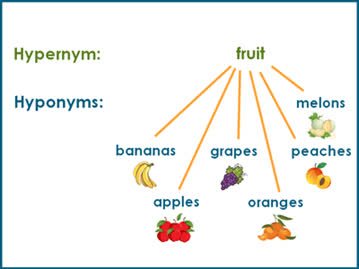
(noun) Hyperonym, Oberbegriff
Beispiel:
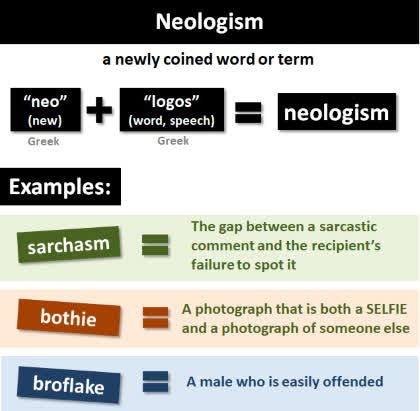
(noun) Neologismus, Wortneuschöpfung
Beispiel:
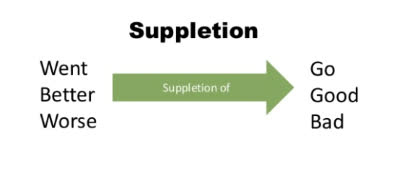
(noun) Suppletion
Beispiel:
(verb) registrieren, anmelden, anzeigen;
(noun) Register, Verzeichnis, Kasse
Beispiel:
(noun) Metathese, Lautverschiebung
Beispiel:
(noun) Reduplikation, Wortverdopplung
Beispiel:
(noun) Schneiden, Stutzen, Zeitungsausschnitt
Beispiel:
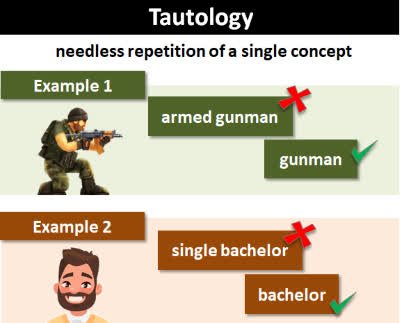
(noun) Tautologie, Wortwiederholung, logische Wahrheit
Beispiel:
(noun) Hyponym, Unterbegriff
Beispiel:
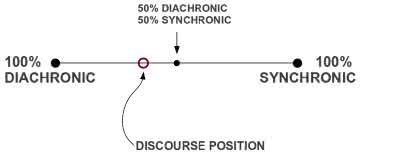
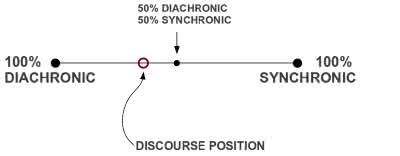
(adjective) synchronisch
Beispiel:
(adjective) diachron
Beispiel: