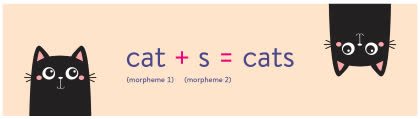Linguistics Vocabulary Set in Level C2: Full and Detailed List
The 'Linguistics' vocabulary set in 'Level C2' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /prəˈlɪk.sə.t̬i/
Example:
The editor advised the writer to reduce the prolixity in his manuscript.
/ˈret̬.ɚ.ɪk/
Example:
His powerful rhetoric swayed the crowd.
/ˈep.ə.θet/
Example:
The king was often referred to by the epithet 'the Great'.
/ˌɪn.t̬ɚ.teks.tʃuˈæl.ə.t̬i/
Example:
The novel exhibits strong intertextuality with classic myths.
/ˌæp.əˈzɪʃ.ən/
Example:
The artist used apposition of bright and dark colors to create contrast.
/pɔːrtˈmæntoʊ wɜːrd/
Example:
The term 'brunch' is a portmanteau word, combining 'breakfast' and 'lunch'.
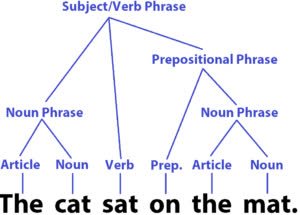
/ˈsɪn.tæks/
Example:
The grammar checker identified an error in the sentence syntax.
/ˈmɔːr.fiːm/
Example:
The word 'unbreakable' contains three morphemes: 'un-', 'break', and '-able'.
/səˈmæn.t̬ɪks/
Example:
The study of semantics helps us understand how language conveys meaning.
/ˈlek.sɪ.kɑːn/
Example:
The legal lexicon can be difficult for laypeople to understand.
/ə.'næf.ə.rə/
Example:
Martin Luther King Jr.'s 'I Have a Dream' speech is famous for its use of anaphora.
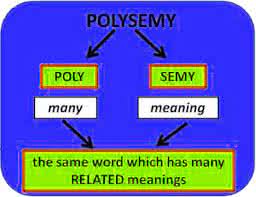
/ˈpɑː.lɪ.siː.mi/
Example:
The word 'bank' is a classic example of polysemy, referring to a financial institution or the side of a river.
/ˈæl.ə.foʊn/
Example:
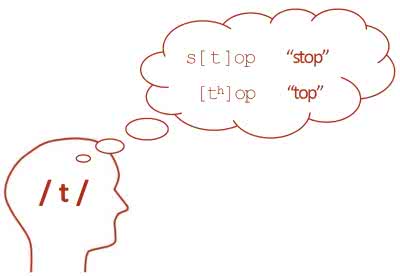
The aspirated 'p' in 'pin' and the unaspirated 'p' in 'spin' are allophones of the phoneme /p/.
/ˈlek.siːm/
Example:
The words 'run', 'runs', 'ran', and 'running' all belong to the same lexeme 'RUN'.
/ˈfoʊ.niːm/
Example:
The word 'cat' has three phonemes: /k/, /æ/, and /t/.
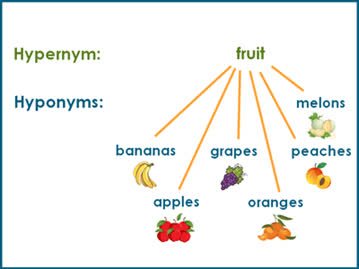
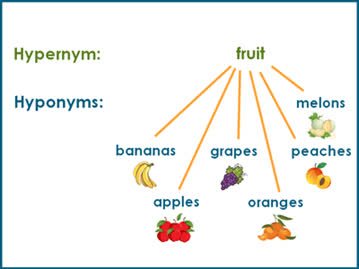
/ˈhaɪ.pɚ.nɪm/
Example:
The word 'animal' is a hypernym of 'dog' and 'cat'.
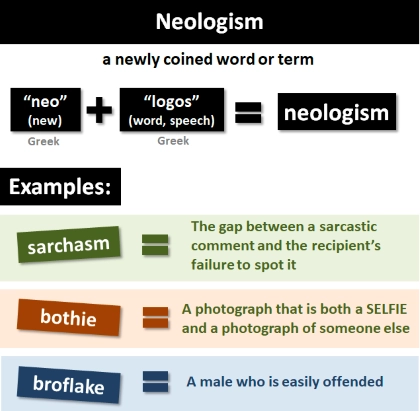
/niˈɑː.lə.dʒɪ.zəm/
Example:
The word 'internet' was once a neologism.
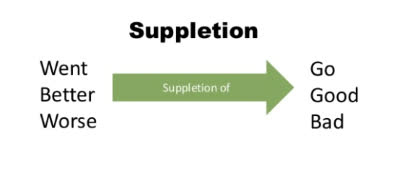
/sʌˈpliːʃən/
Example:
The verb 'go' exhibits suppletion in its past tense form 'went'.
/ˈredʒ.ə.stɚ/
Example:
You need to register your car with the DMV.
/məˈtæθ.ə.sɪs/
Example:
The word 'ask' becoming 'aks' is an example of metathesis.
/riˌduː.pləˈkeɪ.ʃən/
Example:
The word 'hush-hush' is an example of reduplication.
/ˈklɪp.ɪŋ/
Example:
The barber finished the hair clipping quickly.
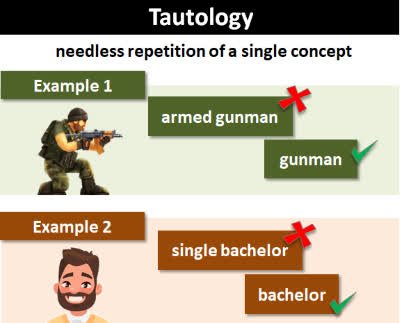
/tɑːˈtɑː.lə.dʒi/
Example:
The phrase 'free gift' is a tautology because a gift is inherently free.
/ˈhaɪ.pə.nɪm/
Example:
In the sentence 'The dog barked loudly,' 'dog' is a hyponym of 'animal.'
/sɪnˈkrɑː.nɪk/
Example:
The linguist conducted a synchronic analysis of modern English.
/ˌdaɪ.əˈkrɑː.nɪk/
Example:
The linguist conducted a diachronic study of English vocabulary.