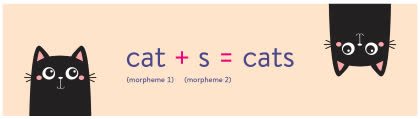词汇集 语言学(属于 C2级别):完整且详细的清单
词汇集「语言学」(属于「C2级别」)从国际标准教材来源精心挑选,帮助您在短时间内掌握词汇。全面汇整定义、例句及标准发音…
在 Lingoland 学习此词汇集
立即学习 /prəˈlɪk.sə.t̬i/
(noun) 冗长, 啰嗦, 冗赘
示例:
The editor advised the writer to reduce the prolixity in his manuscript.
编辑建议作者减少手稿中的冗长。
/ˈep.ə.θet/
(noun) 绰号, 称号, 修饰语
示例:
The king was often referred to by the epithet 'the Great'.
国王常被称为“大帝”这一称号。
/ˌɪn.t̬ɚ.teks.tʃuˈæl.ə.t̬i/
(noun) 互文性
示例:
The novel exhibits strong intertextuality with classic myths.
这部小说与经典神话有着强烈的互文性。
/ˌæp.əˈzɪʃ.ən/
(noun) 并置, 并列, 同位语
示例:
The artist used apposition of bright and dark colors to create contrast.
艺术家运用明暗色彩的并置来创造对比。
/pɔːrtˈmæntoʊ wɜːrd/
(noun) 合成词, 混成词
示例:
The term 'brunch' is a portmanteau word, combining 'breakfast' and 'lunch'.
“早午餐”一词是一个合成词,结合了“早餐”和“午餐”。
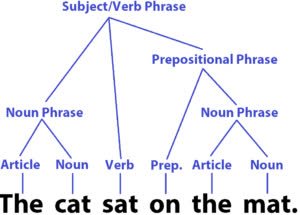
/ˈsɪn.tæks/
(noun) 语法, 句法
示例:
The grammar checker identified an error in the sentence syntax.
语法检查器识别出句子语法中的错误。
/ˈmɔːr.fiːm/
(noun) 语素
示例:
The word 'unbreakable' contains three morphemes: 'un-', 'break', and '-able'.
单词“unbreakable”包含三个语素:“un-”、“break”和“-able”。
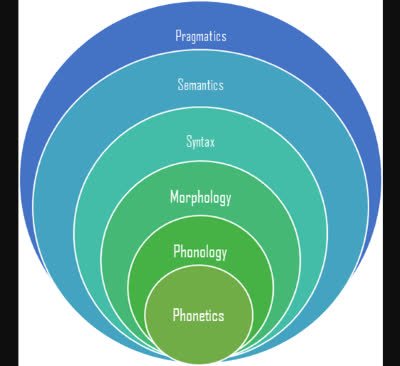
/səˈmæn.t̬ɪks/
(noun) 语义学, 语义, 含义
示例:
The study of semantics helps us understand how language conveys meaning.
语义学的研究帮助我们理解语言如何传达意义。
/ˈlek.sɪ.kɑːn/
(noun) 词汇, 词典, 字典
示例:
The legal lexicon can be difficult for laypeople to understand.
法律词汇对非专业人士来说可能很难理解。
/ə.'næf.ə.rə/
(noun) 首语重复, 排比
示例:
Martin Luther King Jr.'s 'I Have a Dream' speech is famous for its use of anaphora.
马丁·路德·金的《我有一个梦想》演讲因其首语重复的运用而闻名。
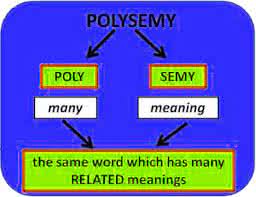
/ˈpɑː.lɪ.siː.mi/
(noun) 多义性
示例:
The word 'bank' is a classic example of polysemy, referring to a financial institution or the side of a river.
“银行”一词是多义性的经典例子,既指金融机构,也指河岸。
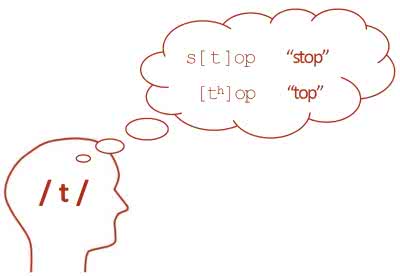
/ˈæl.ə.foʊn/
(noun) 同位异音
示例:
The aspirated 'p' in 'pin' and the unaspirated 'p' in 'spin' are allophones of the phoneme /p/.
“pin”中送气的“p”和“spin”中不送气的“p”是音素/p/的同位异音。
/ˈlek.siːm/
(noun) 词位, 词素
示例:
The words 'run', 'runs', 'ran', and 'running' all belong to the same lexeme 'RUN'.
单词“run”、“runs”、“ran”和“running”都属于同一个词位“RUN”。
/ˈfoʊ.niːm/
(noun) 音素
示例:
The word 'cat' has three phonemes: /k/, /æ/, and /t/.
单词“cat”有三个音素:/k/、/æ/ 和 /t/。
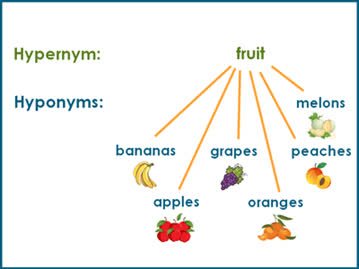
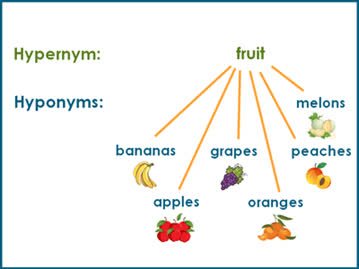
/ˈhaɪ.pɚ.nɪm/
(noun) 上位词, 总称
示例:
The word 'animal' is a hypernym of 'dog' and 'cat'.
“动物”一词是“狗”和“猫”的上位词。
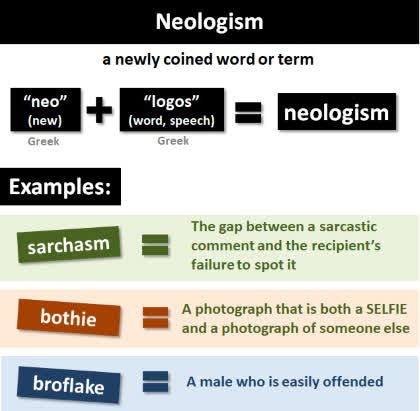
/niˈɑː.lə.dʒɪ.zəm/
(noun) 新词, 新词语
示例:
The word 'internet' was once a neologism.
“互联网”这个词曾经是一个新词。
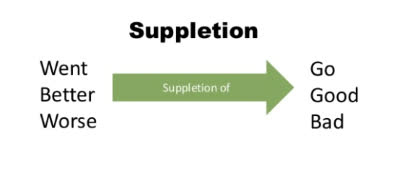
/sʌˈpliːʃən/
(noun) 异干同义, 补充
示例:
The verb 'go' exhibits suppletion in its past tense form 'went'.
动词“go”在过去式“went”中表现出异干同义现象。
/ˈredʒ.ə.stɚ/
(verb) 注册, 登记, 显示;
(noun) 登记簿, 名册, 收银机
示例:
You need to register your car with the DMV.
你需要到车管所注册你的车。
/məˈtæθ.ə.sɪs/
(noun) 音位转换, 音位颠倒
示例:
The word 'ask' becoming 'aks' is an example of metathesis.
单词“ask”变成“aks”是音位转换的一个例子。
/riˌduː.pləˈkeɪ.ʃən/
(noun) 叠词, 重复
示例:
The word 'hush-hush' is an example of reduplication.
“hush-hush”这个词是叠词的一个例子。
/ˈklɪp.ɪŋ/
(noun) 修剪, 剪报, 剪下物
示例:
The barber finished the hair clipping quickly.
理发师很快完成了头发修剪。
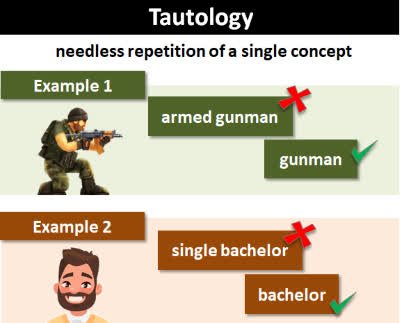
/tɑːˈtɑː.lə.dʒi/
(noun) 同义反复, 赘述, 重言式
示例:
The phrase 'free gift' is a tautology because a gift is inherently free.
“免费赠品”这个短语是同义反复,因为礼物本身就是免费的。
/ˈhaɪ.pə.nɪm/
(noun) 下义词
示例:
In the sentence 'The dog barked loudly,' 'dog' is a hyponym of 'animal.'
在句子“狗大声吠叫”中,“狗”是“动物”的下义词。
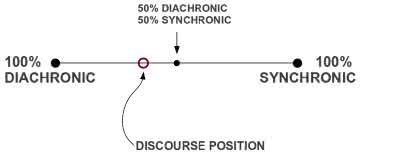
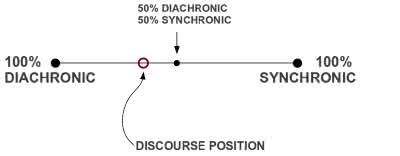
/sɪnˈkrɑː.nɪk/
(adjective) 共时的
示例:
The linguist conducted a synchronic analysis of modern English.
这位语言学家对现代英语进行了共时性分析。
/ˌdaɪ.əˈkrɑː.nɪk/
(adjective) 历时性, 历史的
示例:
The linguist conducted a diachronic study of English vocabulary.
这位语言学家对英语词汇进行了历时性研究。