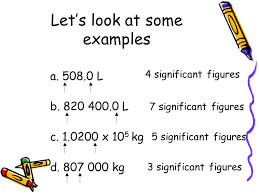化学 内 化学専攻 語彙セット:完全かつ詳細なリスト
「化学」内の「化学専攻」語彙セットは国際標準教材から厳選され、短期間で語彙をマスターできます。定義、例文、標準発音を網羅…
Lingolandでこの語彙セットを学習
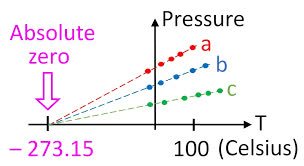
今すぐ学習(noun) 絶対温度
例:
(noun) 絶対零度
例:
(noun) 酸;
(adjective) 酸性の, 酸っぱい
例:
(noun) 土台, 基礎, 根拠;
(verb) 基づく, 基礎を置く;
(adjective) 卑劣な, 下劣な
例:
(adjective) アルカリ性, 塩基性
例:
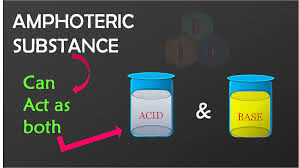
(adjective) 両性
例:
(verb) 引き起こす, 促進する, 早める;
(adjective) 性急な, 軽率な, 早まった;
(noun) 沈殿物, 析出物
例:
(noun) 付加反応
例:
(noun) 吸収, 没頭, 集中
例:
(noun) アルコール, 酒
例:
(noun) 触媒, きっかけ, 促進剤
例:
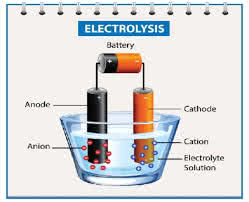
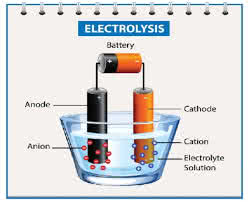
(noun) アノード, 陽極
例:
(noun) カソード, 陰極
例:
(noun) 連鎖反応, 核連鎖反応
例:
(noun) 化学式
例:
(noun) 周回, 巡回, 電気回路
例:
(noun) コンダクタンス, 電気伝導率
例:
(noun) 結露, 凝縮, 要約
例:
(noun) 共有結合
例:
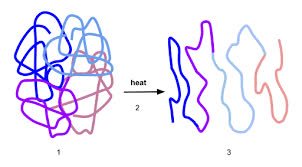
(verb) 変性させる, 性質を変える
例:
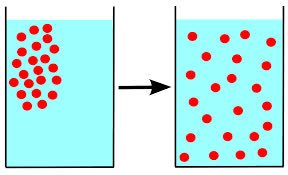
(noun) 普及, 拡散
例:
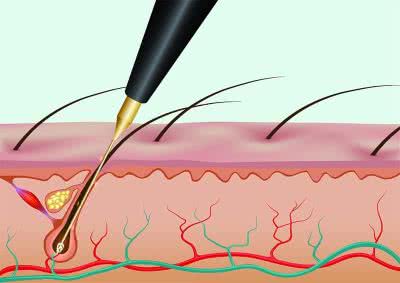
(noun) 電気分解, 電気分解脱毛
例:
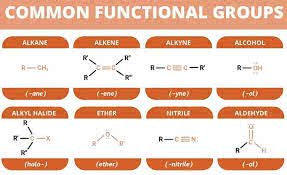
(noun) 官能基
例:
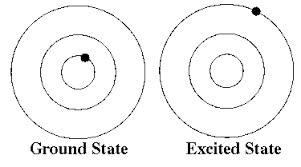
(noun) 基底状態
例:
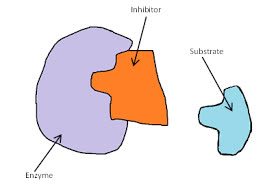
(noun) 阻害剤, 抑制剤, 阻害要因
例:
(noun) 有機化合物
例:
(noun) 圧力, 重圧, プレッシャー;
(verb) 圧力をかける, 強制する
例:
(noun) 製品, 生産物, 積
例:
(noun) 量子論
例:
(adjective) 放射性の
例:
(noun) 塩, 化合物;
(verb) 塩を加える, 塩漬けにする
例:
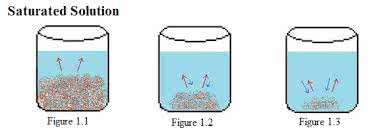
(adjective) 飽和した, 浸された, 満たされた
例:
(noun) 半導体
例:
(noun) 有効数字
例:
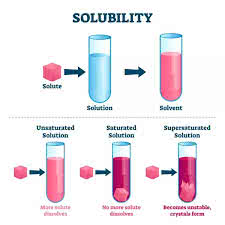
(noun) 溶解度
例:
(adjective) 支払い能力のある, 債務を弁済できる;
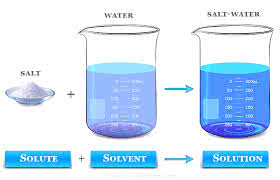
(noun) 溶媒
例:
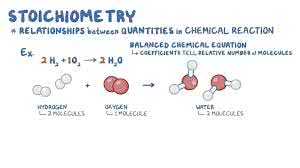
(noun) 化学量論
例:
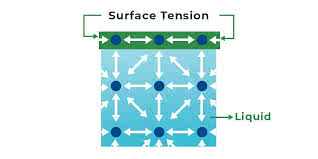
(noun) 表面張力
例:
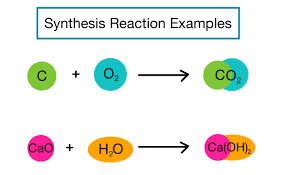
(noun) 統合, 合成, 総合
例:
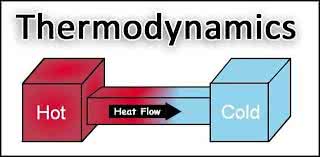
(noun) 熱力学
例:
(noun) 気化, 蒸発
例:
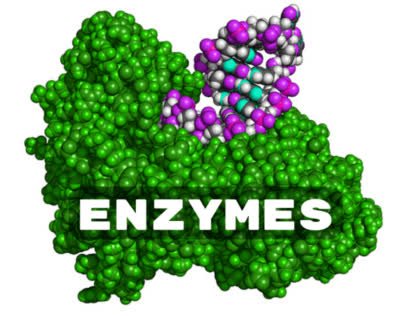
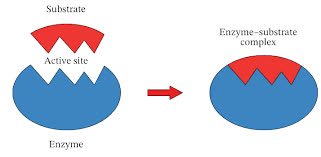
(noun) 酵素
例:
(noun) 異性体
例:
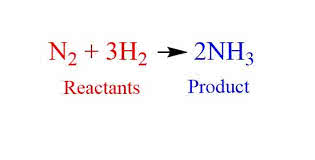
(noun) 反応, 応答, 化学反応
例:
(noun) バランス, 均衡, 残高;
(verb) バランスをとる, 均衡を保つ, 比較検討する
例:
(noun) 公式, 数式, 処方
例:
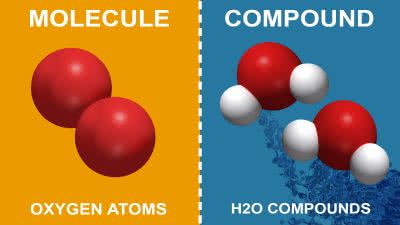
(noun) 分子
例:
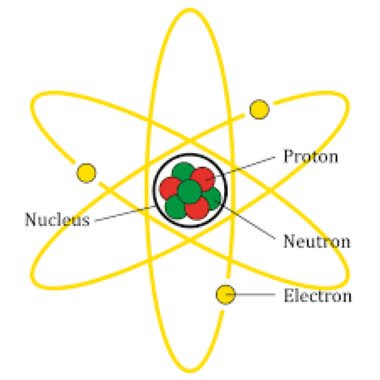
(noun) 原子, 微塵, 少しも
例:
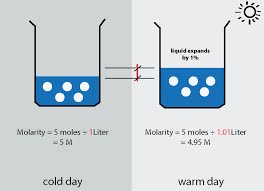
(noun) モル濃度
例:
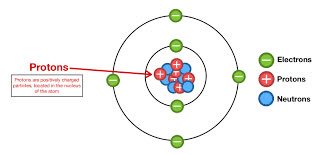
(noun) 陽子
例:
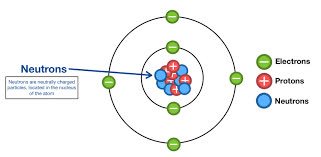
(noun) 中性子
例:
(adjective) 軌道の, 眼窩の
例:
(noun) リトマス, 試金石, 指標
例:
(noun) キレート;
(verb) キレート化する
例:
(noun) 配位子, リガンド
例:
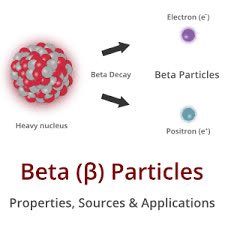
(noun) ベータ粒子
例:
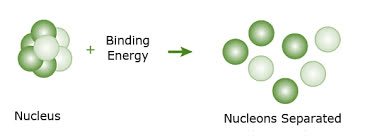
(noun) 結合エネルギー
例:
(noun) 解離, 分離, 乖離
例:
(noun) 流出, 貯留, ほとばしり
例:
(noun) 終点, 最終地点, エンドポイント
例:
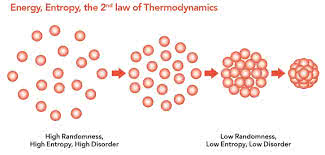
(noun) エントロピー, 情報エントロピー, 無秩序
例:
(noun) 均衡, 平衡, 身体の平衡
例:
(noun) 家族, 家系, 血縁;
(adjective) 家族の
例:
(noun) 運動エネルギー
例:
(noun) 塊, かたまり, 質量;
(verb) 集まる, 集結する;
(adjective) 大量の, 大衆の
例:
(noun) 核子
例:
(adjective) 不安定な, 変動しやすい, 揮発性の
例:
(noun) 周期表
例:
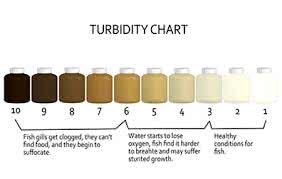
(noun) 濁度, 混濁
例:
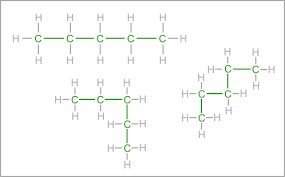
(noun) 炭素鎖
例:
(noun) 化学者, 薬剤師, 薬局
例:
(adjective) 非化学的
例:
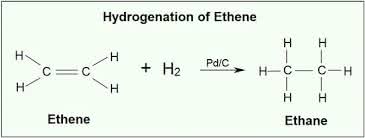
(adjective) 水素添加された
例: