entropy
US /ˈen.trə.pi/
UK /ˈen.trə.pi/
名詞
1.
エントロピー
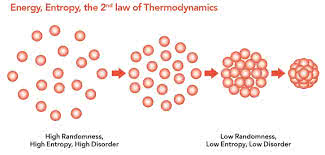
a thermodynamic quantity representing the unavailability of a system's thermal energy for conversion into mechanical work, often interpreted as the degree of disorder or randomness in the system.
例:
•
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system can only increase over time.
熱力学第二法則は、孤立系のエントロピーは時間とともに増加するだけであると述べている。
•
The melting of ice into water is an example of an increase in entropy.
氷が水に溶けるのは、エントロピーの増加の一例である。
2.
情報エントロピー
a measure of the disorder or randomness of information or data.
例:
•
In information theory, entropy quantifies the average unpredictability in a source of data.
情報理論において、エントロピーはデータ源における平均的な予測不可能性を定量化する。
•
High entropy in a message means it is highly unpredictable and contains more information.
メッセージ内の高いエントロピーは、それが非常に予測不可能であり、より多くの情報を含んでいることを意味する。
3.
無秩序, 混乱
lack of order or predictability; gradual decline into disorder.
例:
•
The office descended into complete entropy after the busy week.
忙しい一週間後、オフィスは完全な無秩序に陥った。
•
The city's infrastructure showed signs of increasing entropy.
都市のインフラは、増大する無秩序の兆候を示していた。