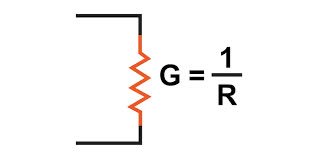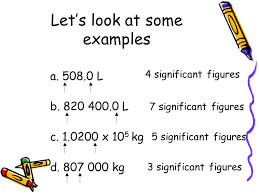Chemistry Major Vocabulary Set in Chemistry: Full and Detailed List
The 'Chemistry Major' vocabulary set in 'Chemistry' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /ˈæb.sə.luːt ˈtem.pər.ə.tʃər/
Example:
Scientists use absolute temperature in many physics calculations.
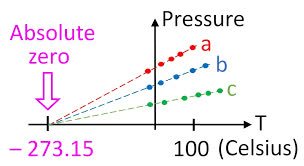
/ˌæb.sə.luːt ˈzɪr.oʊ/
Example:
Scientists are trying to achieve temperatures close to absolute zero in their experiments.
/ˈæk.jɚ.ə.si/
Example:
The report was praised for its accuracy.
/ˈæs.ɪd/
Example:
Sulfuric acid is a strong corrosive substance.
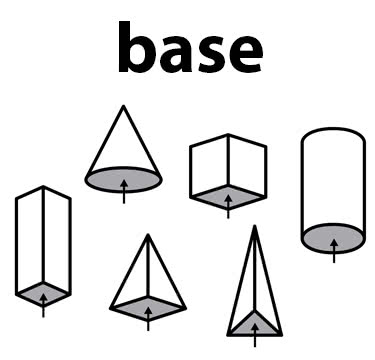
/beɪs/
Example:
The statue stood on a marble base.
/ˈæl.kəl.aɪn/
Example:
Alkaline solutions can neutralize acids.
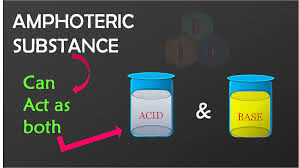
/ˌæmfəˈterɪk/
Example:
Water is an amphoteric substance, as it can act as both an acid and a base.
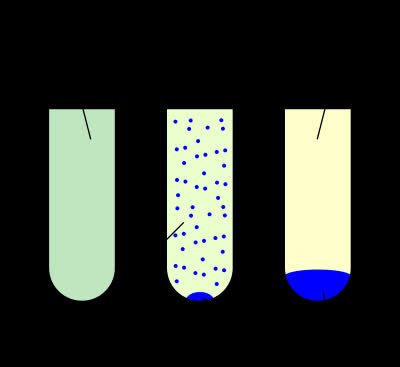
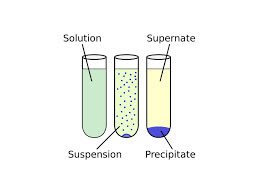
/prɪˈsɪp.ə.teɪt/
Example:
The economic crisis was precipitated by a collapse in housing prices.
/əˈdɪʃ.ən riˈæk.ʃən/
Example:
The hydrogenation of alkenes is a common example of an addition reaction.
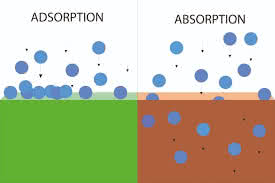
/əbˈzɔːrp.ʃən/
Example:
The sponge is good for the absorption of water.
/ˈæl.kə.hɑːl/
Example:
Drinking too much alcohol can be harmful to your health.
/ˈkæt̬.əl.ɪst/
Example:
Enzymes act as biological catalysts in the body.
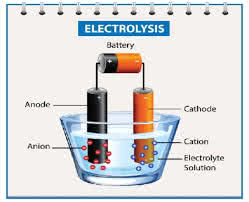
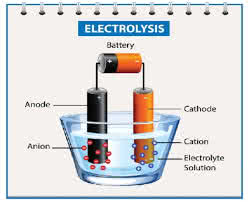
/ˈæn.oʊd/
Example:
In a battery, the anode is where oxidation occurs.
/ˈkæθ.oʊd/
Example:
In a diode, current flows from the anode to the cathode.
/ˈtʃeɪn riˈæk.ʃən/
Example:
The collapse of one bank caused a chain reaction throughout the financial system.
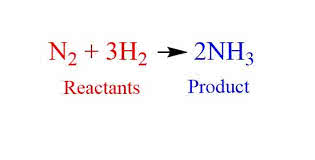
/ˈkɛmɪkəl ɪˈkweɪʒən/
Example:
The teacher wrote a chemical equation on the board to explain the reaction.
/ˈsɝː.kɪt/
Example:
The car completed another circuit of the track.
/kənˈdʌktəns/
Example:
The material's high conductance makes it suitable for electrical wiring.
/ˌkɑːn-/
Example:
You can see condensation on the cold windowpane.
/ˌkoʊ.veɪ.lənt ˈbɑːnd/
Example:
Water molecules are held together by covalent bonds.
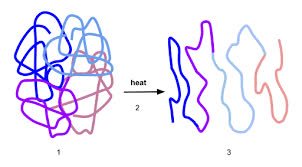
/diːˈneɪ.tʃɚ/
Example:
High heat can denature proteins, causing them to lose their function.
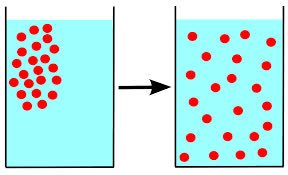
/dɪˈfjuː.ʒən/
Example:
The rapid diffusion of information through the internet has changed society.
/iˌlekˈtrɑː.lə.sɪs/
Example:
Water can be split into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis.
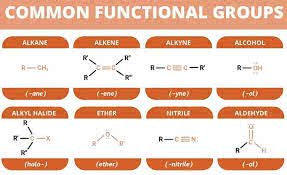
/ˈfʌŋkʃənəl ˌɡruːp/
Example:
The hydroxyl group (-OH) is a common functional group in alcohols.
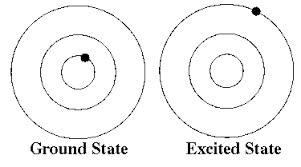
/ˈɡraʊnd steɪt/
Example:
Electrons typically reside in the ground state unless excited by energy.
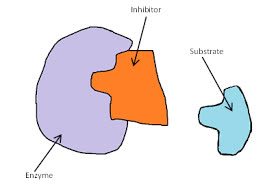
/ɪnˈhɪb.ɪ.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The drug acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme.
/ɔːrˌɡæn.ɪk ˈkɑːm.paʊnd/
Example:
Ethanol is a common organic compound found in alcoholic beverages.
/ˈpreʃ.ɚ/
Example:
The deep sea diver experienced immense pressure.
/ˈprɑː.dʌkt/
Example:
The company launched a new software product.
/ˈkwɑːntəm ˈθiːəri/
Example:
Quantum theory revolutionized our understanding of the universe at the atomic and subatomic levels.
/ˌreɪ.di.oʊˈæk.tɪv/
Example:
The waste material is highly radioactive and must be handled with extreme care.
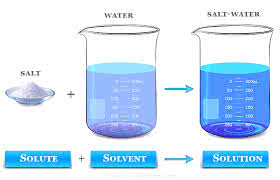
/sɑːlt/
Example:
Add a pinch of salt to the soup for flavor.
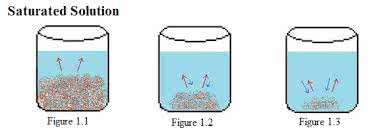
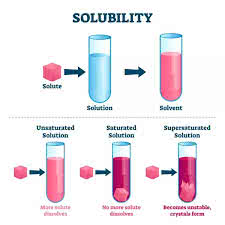
/ˈsætʃ.ər.eɪ.t̬ɪd/
Example:
The ground was saturated after days of heavy rain.
/ˌsem.i.kənˈdʌk.tɚ/
Example:
Silicon is a common semiconductor material used in computer chips.
/ˌsɪɡˈnɪf.ɪ.kənt ˈfɪɡ.ər/
Example:
The measurement 0.0050 has two significant figures.
/ˌsɑːl.jəˈbɪl.ə.t̬i/
Example:
The solubility of sugar in water increases with temperature.
/ˈsɑːl.vənt/
Example:
The company remained solvent despite the economic downturn.
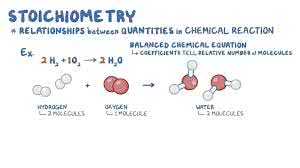
/ˌstɔɪ.kiˈɑː.mə.tri/
Example:
Understanding stoichiometry is crucial for predicting reaction yields.
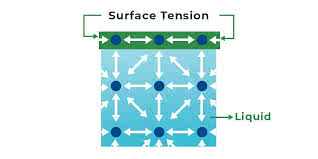
/ˈsɜːr.fɪs ˌten.ʃən/
Example:
Water striders can walk on water due to surface tension.
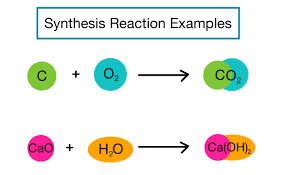
/ˈsɪn.θə.sɪs/
Example:
The report provides a synthesis of the research findings.
/ˈtem.pɚ.ə.tʃɚ/
Example:
The room temperature is 25 degrees Celsius.
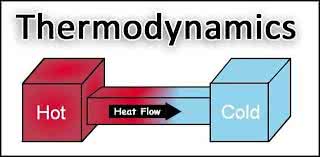
/ˌθɝː.moʊ.daɪˈnæm.ɪks/
Example:
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed.
/ˌveɪ.pɚ.əˈzeɪ.ʃən/
Example:
The vaporization of water occurs at 100 degrees Celsius at standard atmospheric pressure.
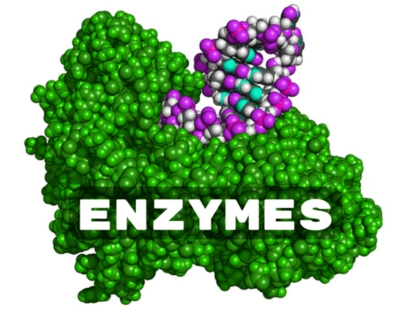
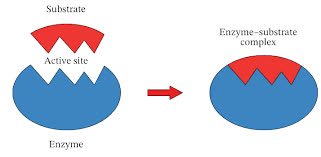
/ˈen.zaɪm/
Example:
Digestion relies on various enzymes to break down food.
/ˈsʌb.streɪt/
Example:
Algae grew on the rocky substrate.
/ˈaɪ.soʊ.mɚ/
Example:
Glucose and fructose are isomers of each other, both having the formula C6H12O6 but different structures.
/riˈæk.ʃən/
Example:
His immediate reaction was to call for help.
/ˈbæl.əns/
Example:
She lost her balance and fell.
/ˈfɔːr.mjə.lə/
Example:
The formula for the area of a circle is πr².
/ˈmɑː.lɪ.kjuːl/
Example:
A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
/ˈæt̬.əm/
Example:
Water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
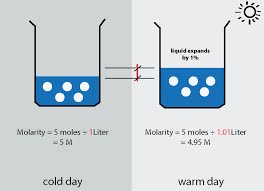
/moʊˈlær·ɪ·t̬i/
Example:
The molarity of the acid solution was determined by titration.
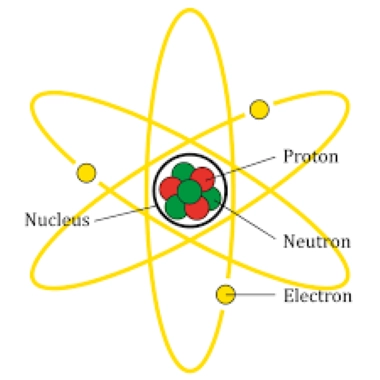
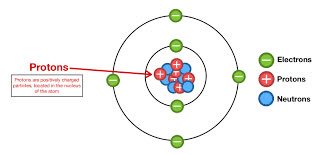
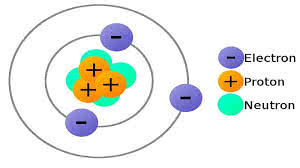
/ˈproʊ.t̬ɑːn/
Example:
The nucleus of a hydrogen atom contains a single proton.
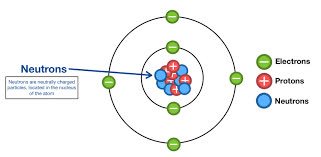
/ˈnuː.trɑːn/
Example:
The nucleus of a helium atom contains two protons and two neutrons.
/iˈlek.trɑːn/
Example:
An electron orbits the nucleus of an atom.
/kwɑːrk/
Example:
Protons and neutrons are made up of quarks.
/ˈɔːr.bɪ.t̬əl/
Example:
The satellite achieved a stable orbital trajectory.
/ˈlɪt.məs/
Example:
The scientist used litmus paper to test the pH of the solution.
/ˈkiː.leɪt/
Example:
The scientist studied the formation of a stable chelate.
/ˈlɪɡ.ənd/
Example:
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom.
/ˈbeɪtə ˌpɑːrtɪkl/
Example:
The radioactive isotope decays by emitting a beta particle.
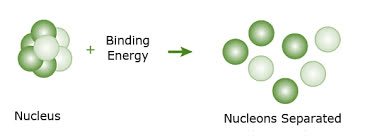
/ˈbaɪndɪŋ ˈenərdʒi/
Example:
The strong nuclear force is responsible for the binding energy of atomic nuclei.
/dɪˌsoʊ.ʃiˈeɪ.ʃən/
Example:
The dissociation of water into hydrogen and oxygen is a chemical process.
/ɪˈfjuː.ʒən/
Example:
The doctor noted a pleural effusion in the patient's lung.
/ˈendˌpɔɪnt/
Example:
The project's endpoint is the successful launch of the new software.
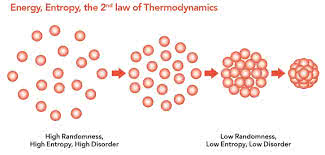
/ˈen.trə.pi/
Example:
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system can only increase over time.
/ˌiː.kwəˈlɪb.ri.əm/
Example:
The market reached a state of equilibrium between supply and demand.
/ˈfæm.əl.i/
Example:
My family is coming to visit next week.
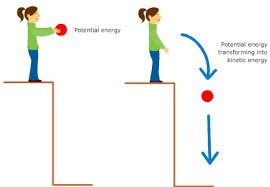
/kɪˌnet.ɪk ˈen.ɚ.dʒi/
Example:
The car's kinetic energy increased as it sped up.
/mæs/
Example:
A huge mass of rock blocked the road.
/ˈnuː.kli.ɑːn/
Example:
The atomic nucleus is composed of nucleons, which are protons and neutrons.
/ˈvɑː.lə.t̬əl/
Example:
The political situation in the region is highly volatile.
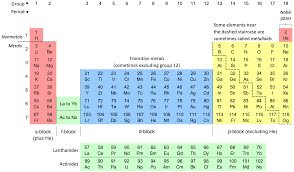
/ðə ˌpɪriˌɑːdɪk ˈteɪbl/
Example:
Students learned about the properties of elements using the periodic table.
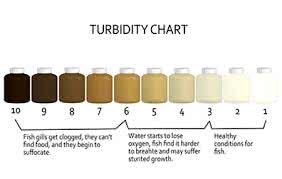
/tɝːˈbɪd.ə.t̬i/
Example:
The high turbidity of the river water made it unsuitable for drinking.
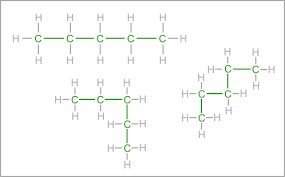
/ˈkɑːr.bən ˌtʃeɪn/
Example:
Long carbon chains are characteristic of fatty acids.
/ˈkem.ɪst/
Example:
The chemist conducted experiments in the lab.
/ˌnɑːnˈkem.ɪ.kəl/
Example:
The farm uses nonchemical methods for pest control.
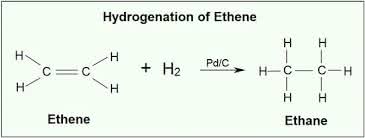
/haɪˈdrɑː.dʒə.neɪ.t̬ɪd/
Example:
Many processed foods contain hydrogenated oils.