Grammar 2 Vocabulary Set in Language: Full and Detailed List
The 'Grammar 2' vocabulary set in 'Language' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /ˈen.dɪŋ/
Example:
The movie had a surprising ending.
/ˌet̬.ɪ.məˈlɑː.dʒɪ.kəl/
Example:
The dictionary includes extensive etymological notes for each word.
/ˌet̬.ɪˈmɑː.lə.dʒi/
Example:
The etymology of the word 'hello' is quite interesting.
/ˌek.skləˈmeɪ.ʃən/
Example:
“Oh no!” was her only exclamation as the vase fell.
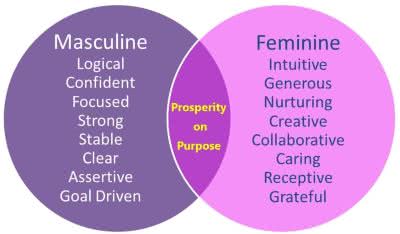
/ˈfem.ə.nɪn/
Example:
She has a very gentle and feminine voice.
/fɔːrm/
Example:
Water can exist in solid, liquid, or gaseous form.
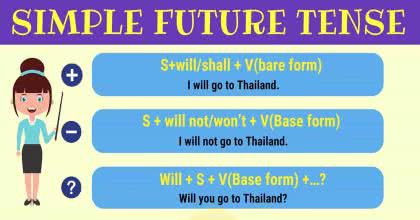
/ˈfjuː.tʃər ˌtens/
Example:
In English, the future tense is often formed with 'will' or 'shall'.
/ˈdʒen.dɚ/
Example:
The company is committed to promoting gender equality in the workplace.
/ˈdʒen.dərˌnuː.trəl/
Example:
The company adopted a gender-neutral dress code.
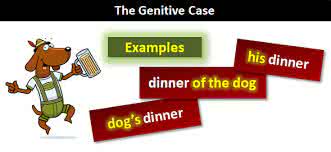
/ˈdʒen.ə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
In English, the apostrophe 's' is often used to form the genitive case, as in 'John's book'.
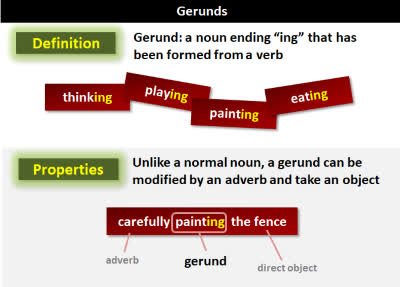
/ˈdʒer.ənd/
Example:
The word 'swimming' is a gerund in the sentence 'Swimming is good exercise.'
/ˈɡræm.ɚ/
Example:
She has an excellent grasp of English grammar.
/ɡrəˈmæt̬.ɪ.kəl/
Example:
The sentence you wrote is perfectly grammatical.
/ˌɪd.i.əˈmæt̬.ɪk/
Example:
Her English is very fluent and idiomatic.
/ɪmˈper.ə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
It is imperative that we act now.
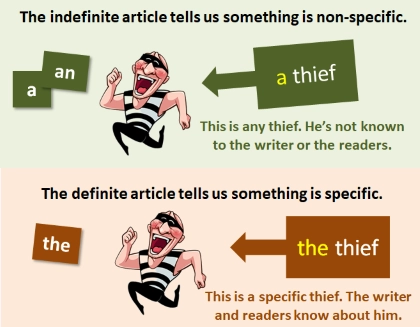
/ɪnˈdɛfɪnɪt ˈɑːrtɪkl/
Example:
In the sentence 'I saw a dog,' 'a' is an indefinite article.
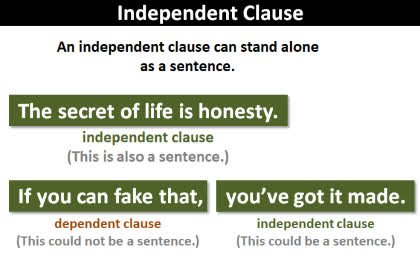
/ˌɪndɪˈpendənt klɔːz/
Example:
An independent clause expresses a complete thought.
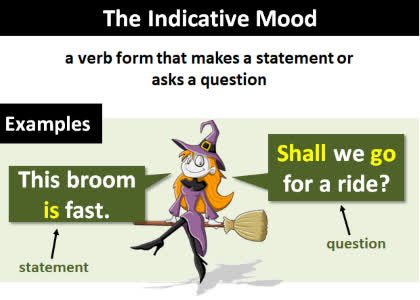
/ɪnˈdɪk.ə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
His poor performance is indicative of a lack of effort.
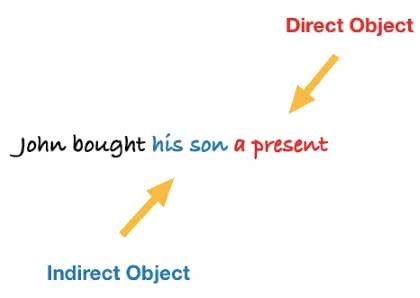
/ɪnˌdaɪ.rekt ˈɑːb.dʒekt/
Example:
In the sentence 'She gave him a book,' 'him' is the indirect object.
/ɪnˌdaɪ.rekt ˈspiːtʃ/
Example:
When reporting a conversation, you often use indirect speech.
/ɪnˈfɪn.ə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
In the sentence 'I want to go home,' 'to go' is an infinitive.
/ɪnˈflek.ʃən/
Example:
The word 'run' has different inflections like 'runs', 'ran', and 'running'.
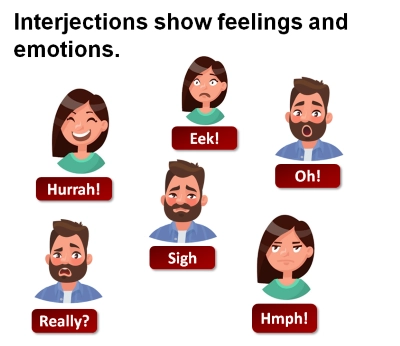
/ˌɪn.t̬ɚˈdʒek.ʃən/
Example:
“Ouch!” he cried, after hitting his thumb with a hammer.
/ˌɪn.t̬əˈrɑː.ɡə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
An interrogative sentence usually ends with a question mark.
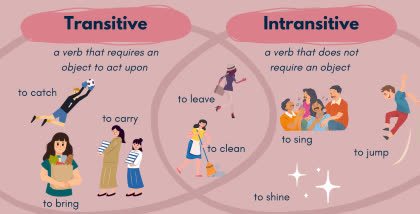
/ɪnˈtræn.sə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
The verb 'sleep' is intransitive.
/ɪˈreɡ.jə.lɚ/
Example:
The coastline is very irregular, with many coves and inlets.
/meɪn klɔːz/
Example:
In the sentence 'Although it was raining, we went for a walk,' 'we went for a walk' is the main clause.
/ˈmæs.kjə.lɪn/
Example:
He has a very masculine voice.
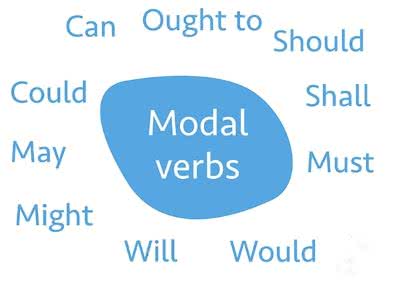
/ˈmoʊ.dəl/
Example:
The architect focused on the modal aspects of the building's design.
/muːd/
Example:
She's been in a bad mood all day.
/ˈneɡ.ə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
She gave a negative answer to the proposal.
/ˈnuː.t̬ɚ/
Example:
In some languages, inanimate objects are assigned a neuter gender.
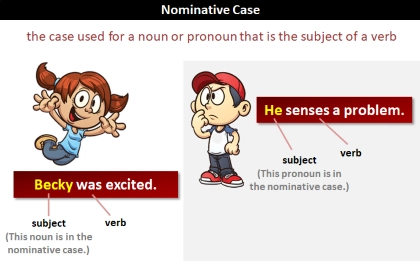
/ˈnɑː.mə.nə.t̬ɪv/
Example:
In Latin, 'puer' is the nominative singular of 'boy'.
/ˈnɑːnˌkaʊnt/
Example:
The word 'information' is a non-count noun.
/ˌnɑːn dɪˈfaɪnɪŋ/
Example:
My brother, who lives in London, is a doctor.
/naʊn/
Example:
In the sentence 'The cat sat on the mat,' 'cat' and 'mat' are nouns.
/ˈnʌm.bɚ/
Example:
Write down your phone number.