SAT理科語彙 内 生物学者 語彙セット:完全かつ詳細なリスト
「SAT理科語彙」内の「生物学者」語彙セットは国際標準教材から厳選され、短期間で語彙をマスターできます。定義、例文、標準発音を網羅…
Lingolandでこの語彙セットを学習
今すぐ学習(noun) 文化, 培養;
(verb) 培養する
例:
(adjective) 代謝の
例:
(noun) 標本, 見本, 典型
例:
(noun) 属, 種類, タイプ
例:
(noun) 負担, 緊張, 品種;
(verb) 酷使する, 緊張させる, 水切りする
例:
(verb) 分泌する, 排出する, 隠す
例:
(verb) 排泄する, 分泌する
例:
(noun) 真核生物
例:
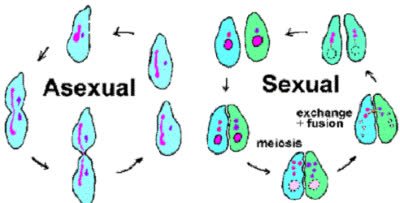
(noun) 無性生殖
例:
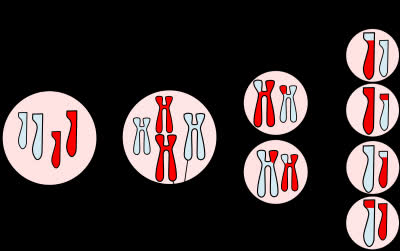
(noun) 減数分裂
例:
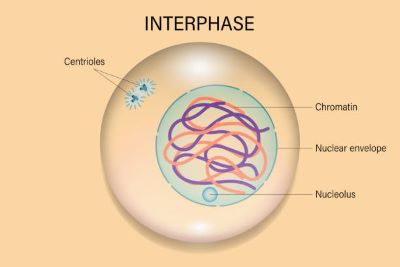
(noun) 間期
例:
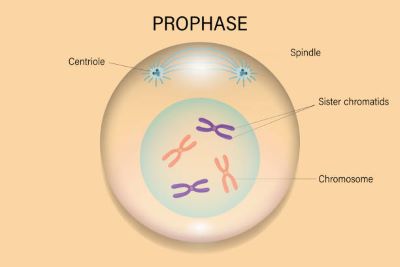
(noun) 前期
例:
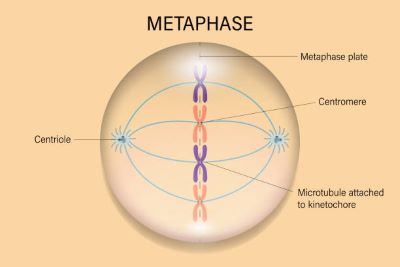
(noun) 中期
例:
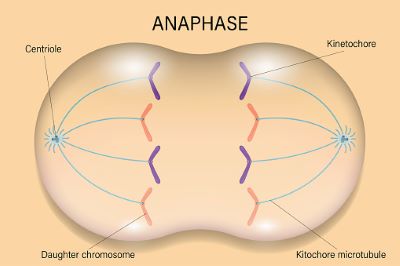
(noun) 後期, アナフェーズ
例:
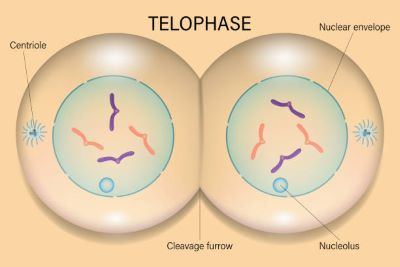
(noun) 終期
例:
(verb) 生物分解する, 自然分解する
例:
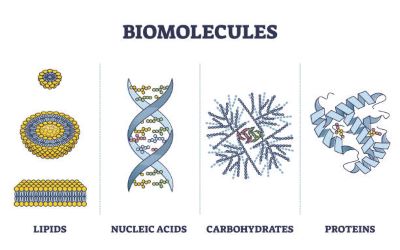
(noun) 生体分子
例:
(noun) 生物多様性
例:
(adjective) 生体適合性のある
例:
(noun) 生体認証, バイオメトリクス
例:
(noun) 生理学者
例:
(noun) 生態学, エコロジー, 環境保護運動
例:
(noun) エコツーリズム
例:
(noun) バイオミミクリー, 生体模倣
例:
(noun) 粘液
例:
(noun) ビリオン, ウイルス粒子
例:
(noun) 条件付け, 訓練, コンディショニング
例:
(noun) 栄養素, 栄養分
例:
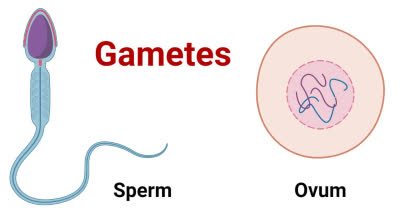
(noun) 配偶子, 生殖細胞
例:
(noun) マイクロバイオーム, 微生物相
例:
(adjective) 人類起源の, 人間活動による
例:
(noun) 運動性, 可動性
例:
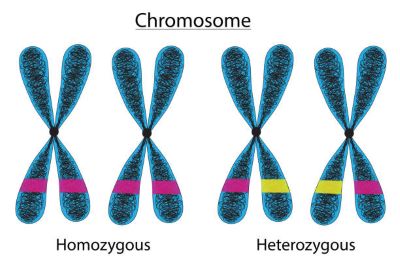
(adjective) 相同の
例:
(noun) 生物発光
例:
(noun) 菌糸体
例:
(adjective) 片利共生の;
(noun) 片利共生生物
例:
(noun) 菌根
例:
(verb) 吸収する, 同化する, 同化させる
例:
(noun) 胞子;
(verb) 胞子を形成する, 胞子を放出する
例:
(noun) バイオマス, 生物量
例:
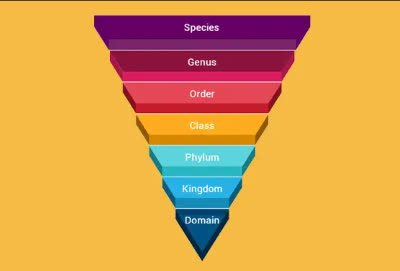
(noun) 分類学, 分類, 分類体系
例:
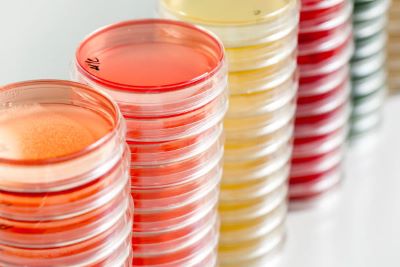
(noun) シャーレ, ペトリ皿
例:
(noun) 宇宙論
例:
(adjective) 毒性の強い, 悪性の, 激しい
例:
(noun) 分解, 腐敗, 分析
例:
(noun) アメーバ
例:
(noun) 適応, 順応, 翻案
例: