Biology Vocabulary Set in SAT Natural Sciences: Full and Detailed List
The 'Biology' vocabulary set in 'SAT Natural Sciences' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /ˈɔːr-/
Example:
Bacteria are single-celled organisms.
/ˈkʌl.tʃɚ/
Example:
Japanese culture is rich in tradition.
/met̬.əˈbɑː.lɪk/
Example:
Exercise can boost your metabolic rate.
/ˈspes.ə.mɪn/
Example:
The museum has a rare specimen of a giant squid.
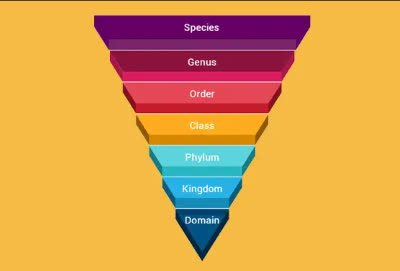
/ˈdʒiː.nəs/
Example:
The genus Homo includes modern humans and several extinct species.
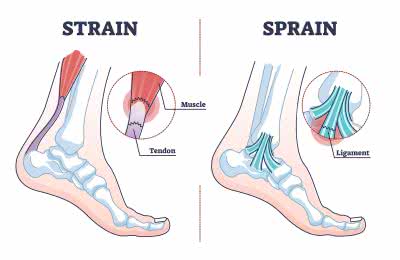
/streɪn/
Example:
The constant pressure put a lot of strain on the bridge.
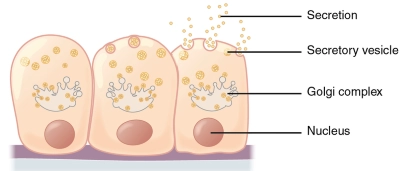
/sɪˈkriːt/
Example:
The glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
/ɪkˈskriːt/
Example:
The kidneys excrete waste products from the body.
/juːˈker.i.oʊt/
Example:
Humans are eukaryotes, as our cells contain a nucleus.
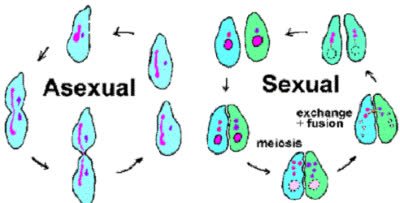
/ˌeɪˌsek.ʃu.əl rɪ.prəˈdʌk.ʃən/
Example:
Many single-celled organisms reproduce through asexual reproduction.
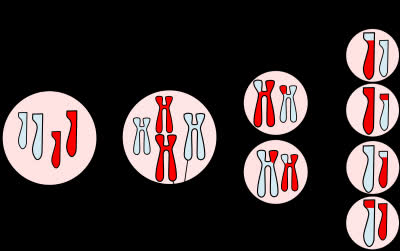
/maɪˈoʊ.sɪs/
Example:
During meiosis, genetic recombination occurs, leading to increased genetic diversity.
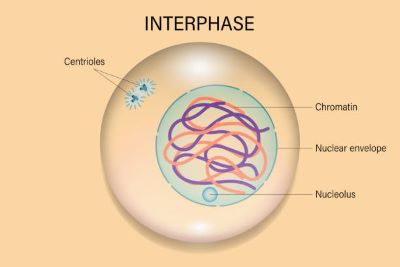
/ˈɪn.t̬ɚ.feɪz/
Example:
During interphase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis.
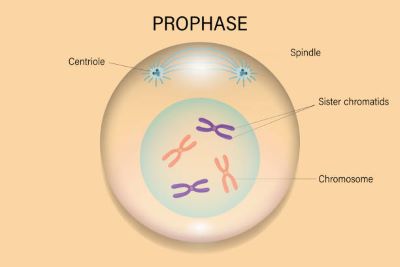
/ˈproʊ.feɪz/
Example:
During prophase, the chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes.
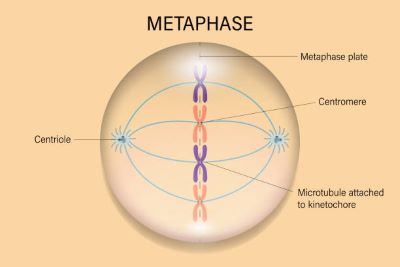
/ˈmet̬.ə.feɪz/
Example:
During metaphase, chromosomes line up along the equatorial plate.
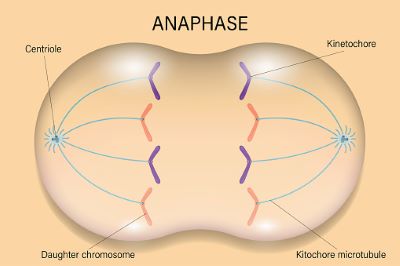
/ˈæn.ə.feɪz/
Example:
During anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell.
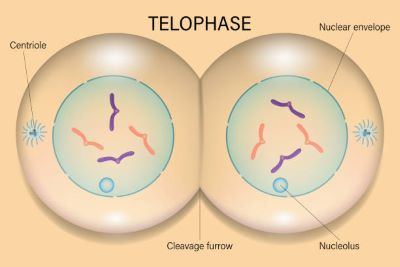
/ˈtiː.lə.feɪz/
Example:
During telophase, the nuclear envelopes reform around the new sets of chromosomes.
/ˌbaɪ.oʊ.dɪˈɡreɪd/
Example:
Most paper products will biodegrade within a few months.
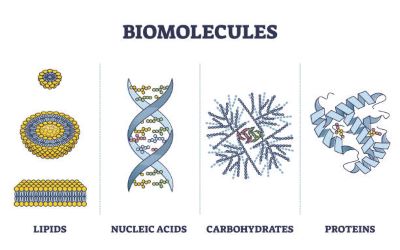
/ˌbaɪ.oʊˈmɑː.lɪ.kjuːl/
Example:
Proteins and nucleic acids are essential biomolecules found in all living cells.
/ˌbaɪ.oʊ.dɪˈvɝː.sə.t̬i/
Example:
Protecting rainforests is crucial for maintaining global biodiversity.
/ˌbaɪ.oʊ.kəmˈpæt̬.ə.bəl/
Example:
The surgeon used a biocompatible material for the implant.
/ˌbaɪ.oʊˈmet.rɪks/
Example:
The airport uses biometrics like facial recognition to speed up security checks.
/ˌmaɪ.kroʊ.baɪˈɑː.lə.dʒi/
/ˌfɪz.iˈɑː.lə.dʒɪst/
Example:
The physiologist explained how the heart responds to extreme exercise.
/iˈkɑː.lə.dʒi/
Example:
She is studying ecology at university.
/ˈiː.koʊˌtʊr.ɪ.zəm/
Example:
Many travelers are choosing ecotourism to experience nature responsibly.
/ˌbaɪ.oʊˈmɪm.ɪ.kri/
Example:
The design of the high-speed train was a result of biomimicry, inspired by the beak of a kingfisher.
/ˈmjuː.kəs/
Example:
When you have a cold, your body produces more mucus.
/ˈvɪr.i.ɑːn/
Example:
The virion attaches to the surface of the host cell to begin the infection process.
/kənˈdɪʃ.ən.ɪŋ/
Example:
The dog's good behavior is a result of consistent conditioning.
/ˈnuː.tri.ənt/
Example:
Plants absorb essential nutrients from the soil.
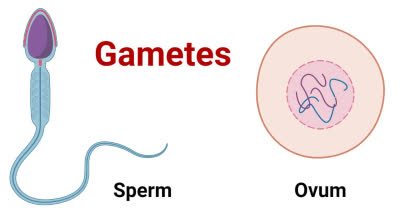
/ˈɡæm.iːt/
Example:
In humans, sperm and egg cells are examples of gametes.
/ˌmaɪ.kroʊˈbaɪ.oʊm/
Example:
Eating fermented foods can help improve your gut microbiome.
/ˌæn.θrə.pəˈdʒen.ɪk/
Example:
Scientists are studying the impact of anthropogenic climate change on marine life.
/moʊˈtɪl.ə.t̬i/
Example:
Sperm motility is a key factor in male fertility.
/hoʊˈmɑː.lə.ɡəs/
Example:
The wings of a bird and the arms of a human are homologous structures.
/ˌbaɪ.oʊ.luː.məˈnes.əns/
Example:
The ocean glowed with the bioluminescence of tiny plankton.
/maɪˈsiːliəm/
Example:
The forest floor was covered with a dense network of fungal mycelium.
/kəˈmen.səl/
Example:
Remora fish have a commensal relationship with sharks.
/ˌmaɪ.kəˈraɪ.zə/
Example:
The health of the forest depends on the mycorrhiza connecting the trees.
/əˈsɪm.ə.leɪt/
Example:
It's hard to assimilate all the new information at once.
/spɔːr/
Example:
Mushrooms reproduce by releasing tiny spores.
/ˈbaɪ.oʊˌmæs/
Example:
The power plant generates electricity from agricultural biomass.
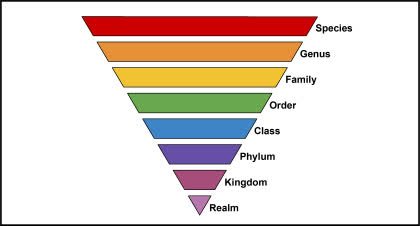
/tækˈsɑː.nə.mi/
Example:
The taxonomy of plants is a complex field.
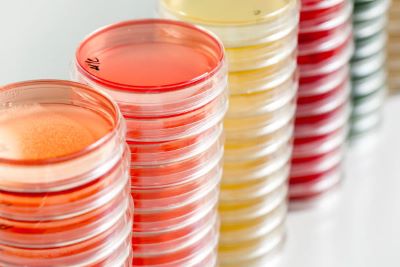
/ˈpiː.tri ˌdɪʃ/
Example:
The scientist placed the bacteria sample in a Petri dish.
/ˈeɪ.ɡɑːr/
Example:
The bacteria grew well on the agar plate.
/kɑːzˈmɑː.lə.dʒi/
Example:
Modern cosmology is based on the Big Bang theory.
/ˈvɪr.jə.lənt/
Example:
The disease was caused by a highly virulent strain of bacteria.
/ˌdiː.kɑːm.pəˈzɪʃ.ən/
Example:
The rapid decomposition of organic matter enriches the soil.
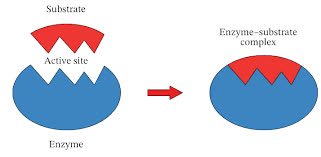
/ˈsʌb.streɪt/
Example:
Algae grew on the rocky substrate.
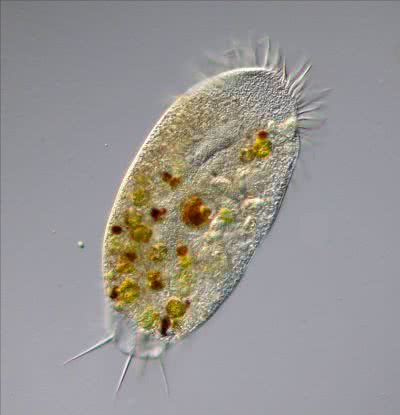
/əˈmiː.bə/
Example:
The ameba moved slowly across the microscope slide.
/ˌæd.əpˈteɪ.ʃən/
Example:
The adaptation of the species to the new environment was slow.