Geometry Vocabulary Set in SAT Math and Logic: Full and Detailed List
The 'Geometry' vocabulary set in 'SAT Math and Logic' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /sloʊp/
Example:
The house is built on a steep slope.
/ɑːrk/
Example:
The bridge has a beautiful arc.
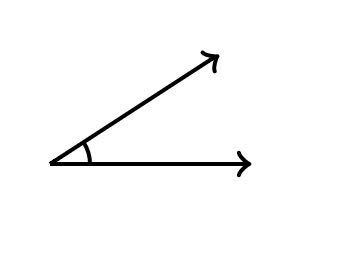
/ˈæŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
The two roads meet at a sharp angle.
/ˈreɪ.di.əns/
Example:
The sun's radiance warmed the earth.
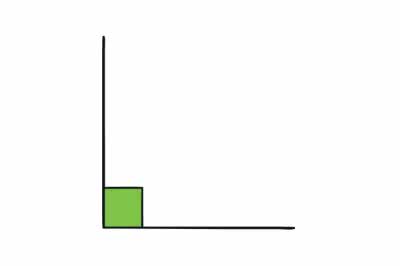
/ˌraɪt ˈæŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
The two walls meet at a perfect right angle.
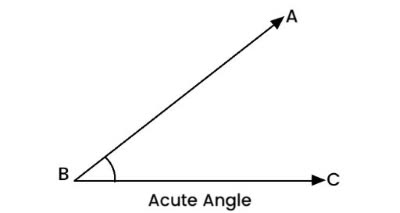
/əˈkjuːt ˈæŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
A triangle with three acute angles is called an acute triangle.
/ˈpɑː.li.ɡɑːn/
Example:
A square is a type of regular polygon with four equal sides and four right angles.
/ˌper.əˈlel.ə.ɡræm/
Example:
A square is a special type of parallelogram.
/ˌkwɑː.drəˈlæt̬.ɚ.əl/
Example:
A square is a type of quadrilateral with four equal sides.
/haɪˈpɝː.bəl.ə/
Example:
The graph of the equation y = 1/x is a hyperbola.
/pəˈræb.əl.ə/
Example:
The path of a projectile under the influence of gravity follows a parabola.
/ˈrɑːm.bəs/
Example:
The artist used a rhombus shape in the abstract painting.
/-t̬ə.ɡɑːn/
Example:
The architect designed a building in the shape of a pentagon.
/ˌtet.rəˈhiː.drən/
Example:
A regular tetrahedron is a pyramid with a triangular base.
/ˈtræp.ɪ.zɔɪd/
Example:
The architect designed the building with a trapezoid base.
/ˌiː.kwəˈlæt̬.ɚ.əl ˈtraɪ.æŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
In an equilateral triangle, every angle measures 60 degrees.
/ˈraɪt ˈtraɪˌæŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
The Pythagorean theorem applies to a right triangle.
/əˈkjuːt ˈtraɪ.æŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
In an acute triangle, every angle measures less than 90 degrees.
/aɪˌsɑː.sə.liːz ˈtraɪ.æŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the equal sides are also equal.
/ˈskeɪ.liːn ˈtraɪ.æŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
In a scalene triangle, all three internal angles are also different.
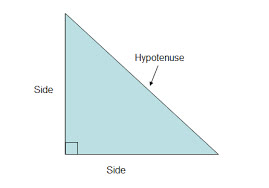
/haɪˈpɑː.t̬ə.nuːz/
Example:
In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
/beɪs/
Example:
The statue stood on a marble base.
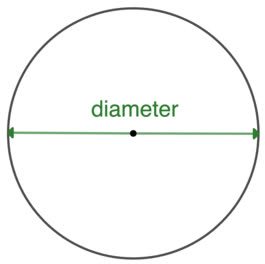
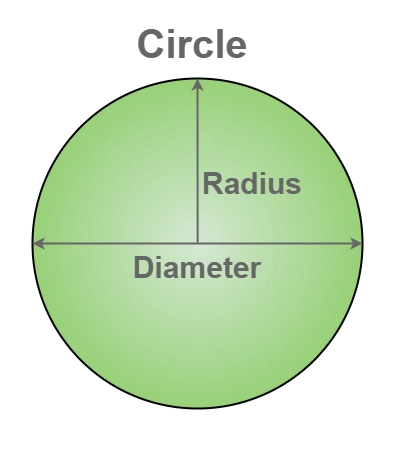
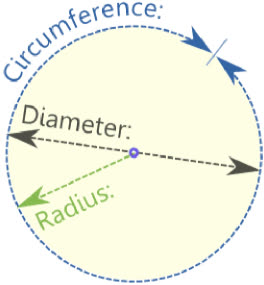
/daɪˈæm.ə.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The diameter of the circle is 10 centimeters.
/ˈreɪ.di.əs/
Example:
The radius of the circle is 5 cm.
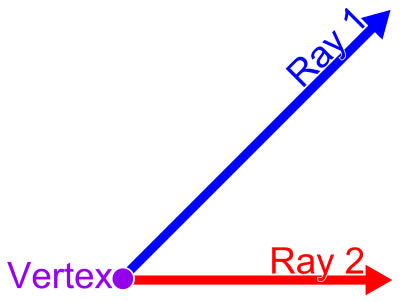
/ˈvɝː.t̬eks/
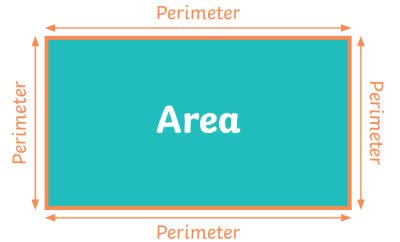
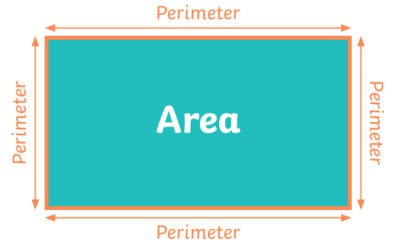
/pəˈrɪm.ə.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
/sɚˈkʌm.fɚ.əns/
Example:
The circumference of the earth is about 24,901 miles.
/ˈer.i.ə/
Example:
The city has a large industrial area.
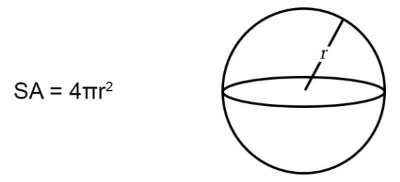
/ˈsɝː.fəs ˌer.i.ə/
Example:
To calculate the surface area of a cube, you multiply the area of one face by six.
/ˈvɑːl.juːm/
Example:
The volume of the box is 10 cubic meters.
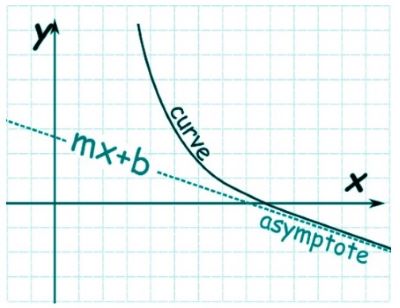
/ˈæs.ɪm.toʊt/
Example:
The graph of the function has a horizontal asymptote at y = 0.
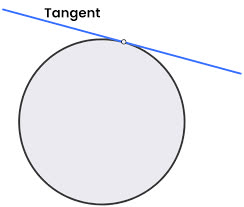
/ˈtæn.dʒənt/
Example:
The speaker went off on a tangent about his childhood.
/prəˈtræk.tɚ/
Example:
She used a protractor to draw a perfect 60-degree angle.
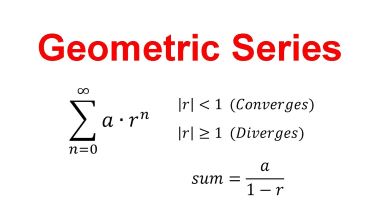
/ˌdʒiː.əˈmet.rɪk ˈsɪr.iːz/
Example:
The sum of an infinite geometric series can be calculated if the common ratio is less than one.
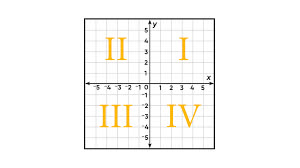
/ˈkwɑː.drənt/
Example:
The graph is divided into four quadrants.
/ɪnˈtɪr.i.ɚ ˈæŋ.ɡəl/
Example:
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
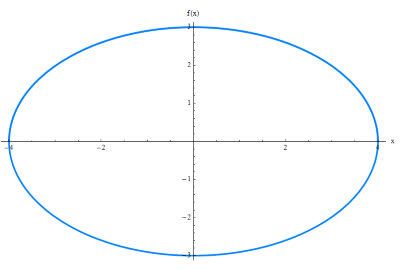
/iˈlɪps/
Example:
The planet orbits the sun in an ellipse.
/kɔːrd/
Example:
The song began with a simple piano chord.
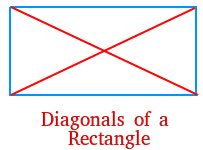
/daɪˈæɡ.ən.əl/
Example:
Draw a diagonal line from one corner to the other.
/kəŋˈɡru.ənt/
Example:
His actions were not congruent with his words.
/ˈper.ə.lel/
Example:
The two roads run parallel to each other.
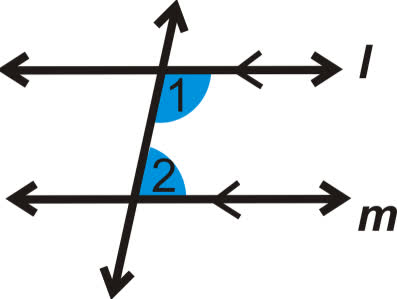
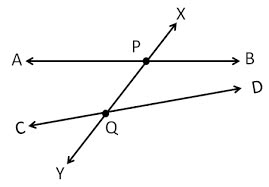
/trænsˈvɝː.səl/
Example:
In geometry, a transversal is a line that passes through two or more other lines.
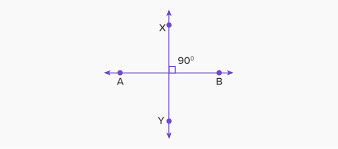
/ˌpɝː.pənˈdɪk.juː.lɚ/
Example:
The wall is perpendicular to the floor.
/baɪˈsekt/
Example:
The river bisects the town.
/trænsˈleɪt/
Example:
Can you translate this document from English to Spanish?
/eɪˈsɪm.ə.tri/
Example:
The architect intentionally designed the building with a striking asymmetry.