entropy
US /ˈen.trə.pi/
UK /ˈen.trə.pi/
名词
1.
熵
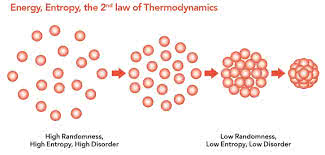
a thermodynamic quantity representing the unavailability of a system's thermal energy for conversion into mechanical work, often interpreted as the degree of disorder or randomness in the system.
示例:
•
The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system can only increase over time.
热力学第二定律指出,孤立系统的熵只能随时间增加。
•
The melting of ice into water is an example of an increase in entropy.
冰融化成水是熵增加的一个例子。
2.
信息熵
a measure of the disorder or randomness of information or data.
示例:
•
In information theory, entropy quantifies the average unpredictability in a source of data.
在信息论中,熵量化了数据源的平均不可预测性。
•
High entropy in a message means it is highly unpredictable and contains more information.
消息中的高熵意味着它高度不可预测并包含更多信息。
3.
混乱, 无序
lack of order or predictability; gradual decline into disorder.
示例:
•
The office descended into complete entropy after the busy week.
忙碌的一周过后,办公室陷入了彻底的混乱。
•
The city's infrastructure showed signs of increasing entropy.
城市的基础设施显示出日益增加的混乱迹象。