Brain Vocabulary Set in Body: Full and Detailed List
The 'Brain' vocabulary set in 'Body' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
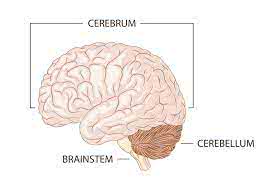
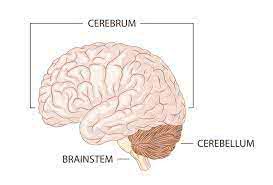
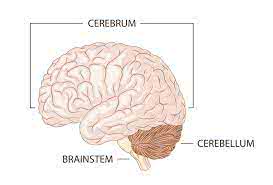
Learn Now /səˈriː.brəm/
Example:
The largest part of the human brain is the cerebrum.
/ˌser.əˈbel.əm/
Example:
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in balance and coordination.
/ˈbreɪn.stem/
Example:
Damage to the brainstem can be life-threatening.
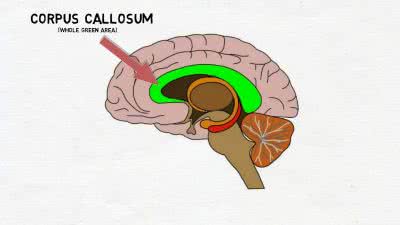
/ˌkɔːr.pəs kəˈloʊ.səm/
Example:
The corpus callosum facilitates communication between the left and right sides of the brain.
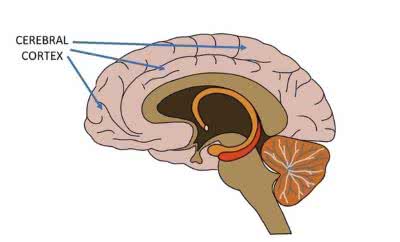
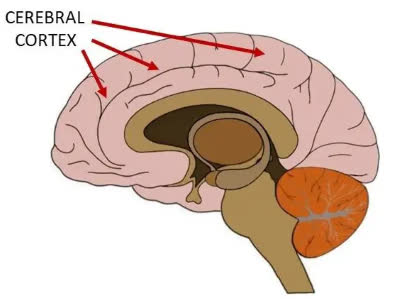
/ˈkɔːr.teks/
Example:
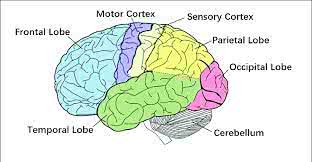
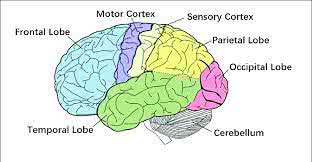
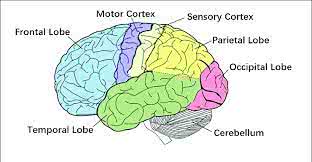
The frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex is involved in planning and decision-making.
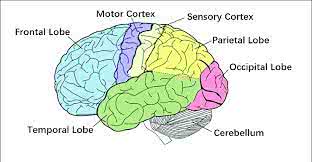
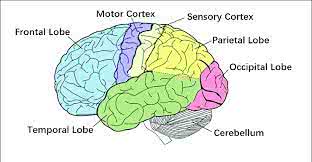
/ˈmoʊ.t̬ɚ ˌkɔːr.teks/
Example:
Damage to the motor cortex can lead to paralysis.
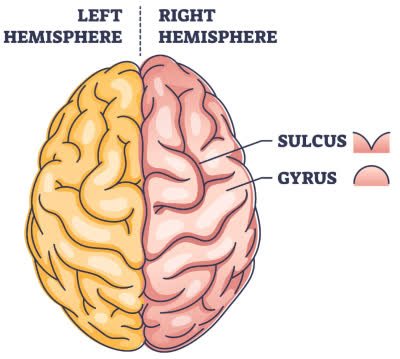
/ˈdʒaɪ.rəs/
Example:
The superior temporal gyrus is involved in auditory processing.
/ˈfrʌn.təl loʊb/
Example:
Damage to the frontal lobe can affect a person's personality and executive functions.
/ˌɑːk.sɪˈpɪt.əl ˌloʊb/
Example:
Damage to the occipital lobe can lead to visual impairments.
/pəˈraɪ.ɪ.təl loʊb/
Example:
Damage to the parietal lobe can affect a person's ability to recognize objects by touch.
/ˈtɛmpərəl loʊb/
Example:
Damage to the temporal lobe can affect memory and language skills.
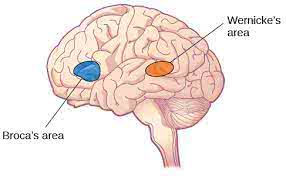
/ˈbroʊkəz ˌɛriə/
Example:
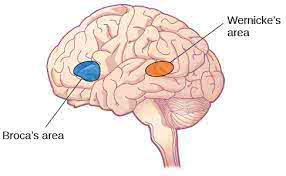
Damage to Broca's area can result in expressive aphasia, where a person has difficulty producing language.
/ˈwɜːrnɪkiz ˌeriə/
Example:
Damage to Wernicke's area can lead to difficulties in understanding spoken language.
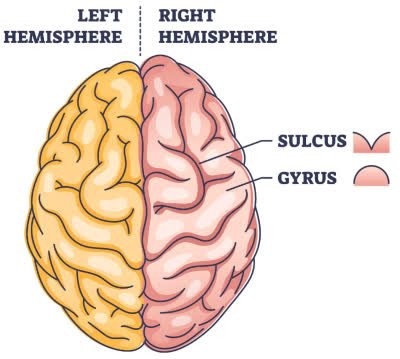
/ˈsʌl.kəs/
Example:
The central sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain.
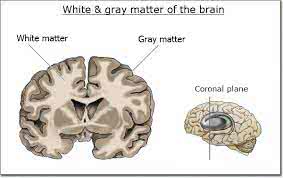
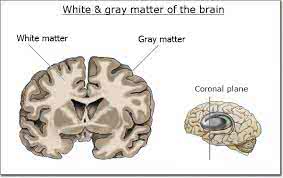
/ˌɡreɪ ˈmæt.ər/
Example:
The neurologist examined the patient's grey matter for abnormalities.
/ˈwaɪt ˌmæt.ər/
Example:
Damage to the white matter can impair cognitive function.
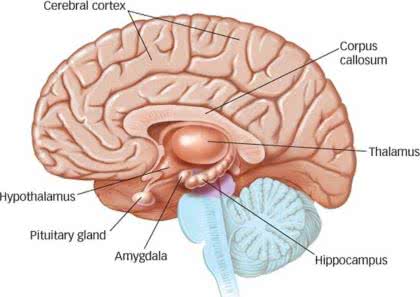
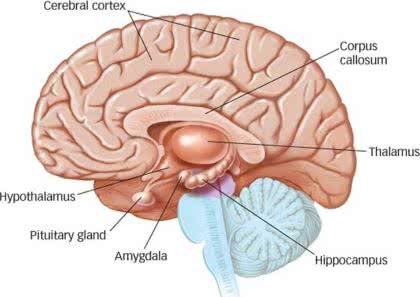
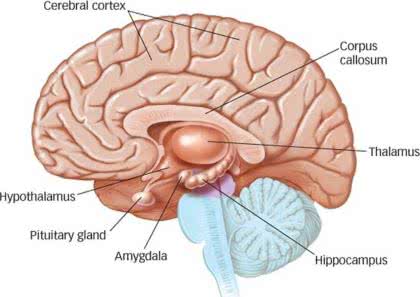
/ˌhaɪ.poʊˈθæl.ə.məs/
Example:
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature.
/ˈθæl.ə.məs/
Example:
The thalamus acts as a relay station for sensory information.
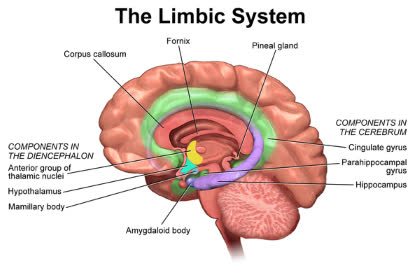
/ˈlɪm.bɪk ˌsɪs.təm/
Example:
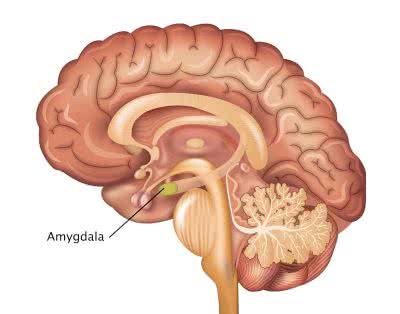
The amygdala, a key part of the limbic system, plays a crucial role in processing emotions like fear.
/əˈmɪɡ.də.lə/
Example:
The amygdala plays a key role in processing fear.
/ˌhɪp.əˈkæm.pəs/
Example:
Damage to the hippocampus can impair the formation of new memories.
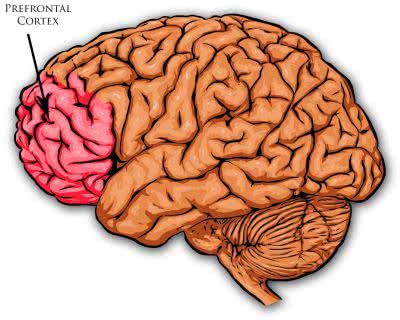
/ˌpriːˈfrʌn.təl ˈkɔːr.teks/
Example:
Damage to the prefrontal cortex can affect a person's ability to make sound decisions.
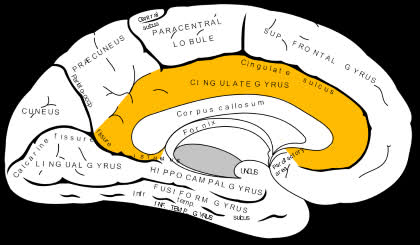
/ˈsɪŋɡjəleɪt ˈdʒaɪrəs/
Example:
The cingulate gyrus plays a crucial role in emotional regulation.
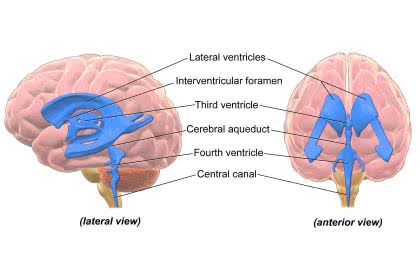
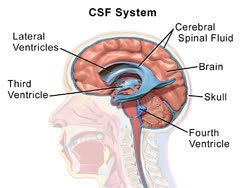
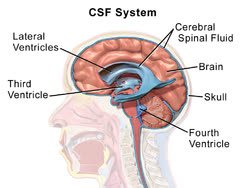
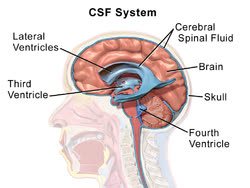
/ˈven.trɪ.kəl/
Example:
The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
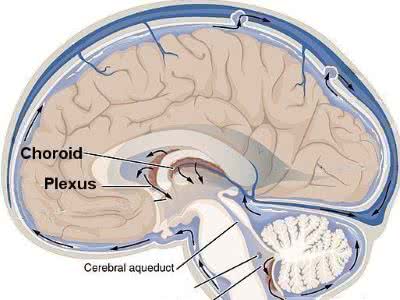
/ˈkɔrɔɪd ˈplɛksəs/
Example:
The choroid plexus is essential for the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
/ˌser.ə.broʊˌspaɪ.nəl ˈfluː.ɪd/
Example:
The doctor ordered a lumbar puncture to analyze the patient's cerebrospinal fluid.
/θɜrd ˈven.trɪ.kl̩/
Example:
Cerebrospinal fluid flows from the lateral ventricles into the third ventricle.
/ˈfɔːrθ ˈven.trɪ.kl̩/
Example:
The fourth ventricle is crucial for the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
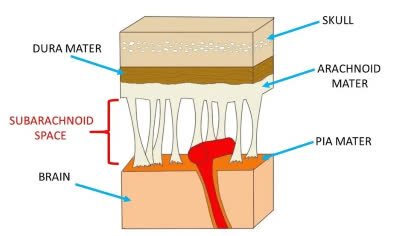
/ˌsʌb.əˈræk.nɔɪd ˌspeɪs/
Example:
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates within the subarachnoid space.
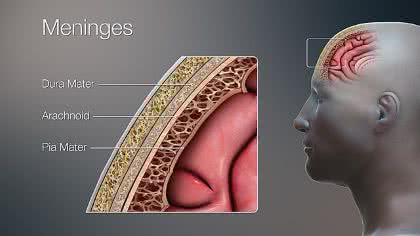
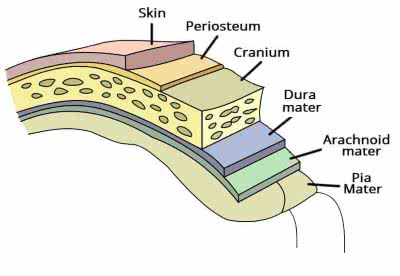
/mɪˈnɪndʒiːz/
Example:
Inflammation of the meninges can lead to meningitis.
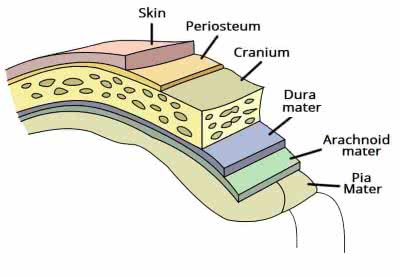
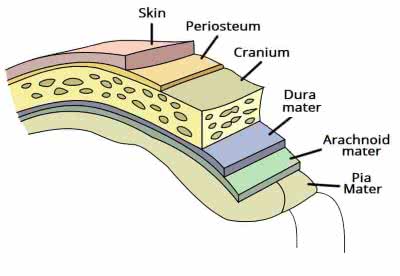
/ˈdʊrə ˈmeɪtər/
Example:
The neurosurgeon carefully incised the dura mater to access the brain.
/əˈræk.nɔɪd/
Example:
The delicate arachnoid membrane covers the brain.
/ˌpiːə ˈmɑːtər/
Example:
The surgeon carefully incised the pia mater to access the brain tissue.
/səˌriː.brəl ˈkɔːr.teks/
Example:
Damage to the cerebral cortex can impair cognitive functions.