Physics Vocabulary Set in SAT Natural Sciences: Full and Detailed List
The 'Physics' vocabulary set in 'SAT Natural Sciences' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
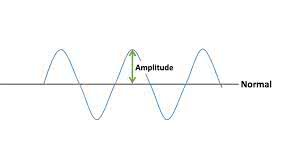
Learn Now /ˈæm.plə.tuːd/
Example:
The amplitude of the sound wave determines its loudness.
/əˈkuː.stɪk/
Example:
The concert hall has excellent acoustic properties.
/ˈsoʊ.nɑːr/
Example:
The submarine used sonar to navigate through the deep ocean.
/ˈprɪz.əm/
Example:
The light was refracted as it passed through the glass prism.
/ˌɪn.frəˈred/
/ˌʌl.trəˈvaɪə.lət/
/flɔːˈres.əns/
Example:
The minerals showed a bright green fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
/spekˈtrɑː.mə.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The scientist used a spectrometer to identify the chemical composition of the sample.
/ˈfoʊ.tɑːn/
Example:
Light is composed of tiny particles called photons.
/rɪˈfrækt/
Example:
The prism will refract the light into a spectrum of colors.
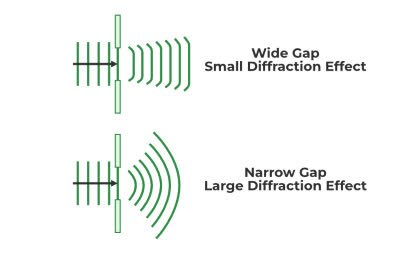
/dɪˈfræk.ʃən/
Example:
Light diffraction causes the rainbow patterns seen on CDs.
/ˌθɝː.moʊ.daɪˈnæm.ɪks/
Example:
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed.
/ˈθɝː.mə.stæt/
Example:
She adjusted the thermostat to make the room warmer.
/ˌkæl.əˈrɪm.ə.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The scientist used a calorimeter to determine the energy content of the food sample.
/θɚˈmɑː.mə.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The nurse used a thermometer to check the patient's temperature.
/ˈmaɪ.kroʊ.tʃɪp/
Example:
The computer's performance is largely dependent on the speed of its microchip.
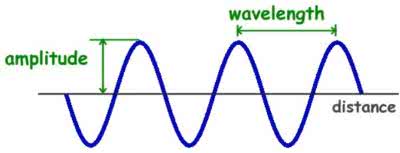
/ˈweɪv.leŋθ/
Example:
The color red has a longer wavelength than blue.
/ˌrel.əˈtɪv.ə.t̬i/
Example:
The concept of moral relativity suggests that right and wrong are not absolute.
/ˈæn.t̬iˌmæt̬.ɚ/
Example:
Scientists are studying antimatter to understand the early universe.
/səˈlɪd.ə.faɪ/
Example:
The lava began to solidify as it cooled.
/ˈlɪk.wə.faɪ/
Example:
Gases must be cooled to extremely low temperatures to liquefy.
/ˌsʌb.əˈtɑː.mɪk/
Example:
Physicists study subatomic particles to understand the fundamental nature of the universe.
/nuːˈtriː.noʊ/
Example:
Scientists detected a neutrino from a distant galaxy.
/ˈnænoʊˌskeɪl/
Example:
At the nanoscale, materials can exhibit very different physical properties.
/məˈtrɑː.lə.dʒi/
Example:
Metrology plays a crucial role in quality control for manufacturing.
/dɪˈfjuːz/
Example:
The scent of flowers diffused throughout the room.
/ˈboʊ.sən/
Example:
The Higgs boson is sometimes called the 'God particle'.
/kəˈlaɪ.dɚ/
Example:
The Large Hadron Collider is the world's largest and most powerful particle accelerator.
/ˈdaɪ.poʊl/
Example:
The water molecule acts as an electric dipole.
/ˈlep.tɑːn/
Example:
The electron is a fundamental lepton.