Biology Vocabulary Set in IELTS Academic (Band 8-9): Full and Detailed List
The 'Biology' vocabulary set in 'IELTS Academic (Band 8-9)' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
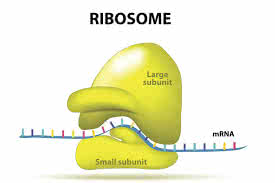
Learn Now /ˈraɪ.bə.soʊm/
Example:
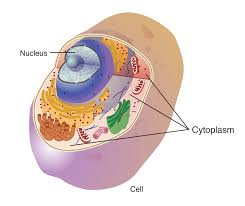
Proteins are synthesized on the ribosomes in the cell's cytoplasm.
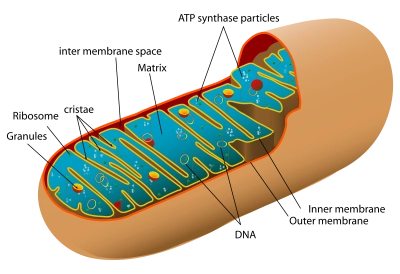
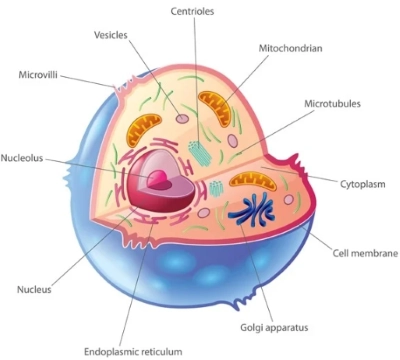
/ˌmaɪ.t̬oʊˈkɑːn.dri.ən/
Example:
The mitochondrion is often called the powerhouse of the cell.
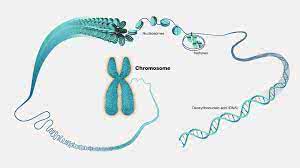
/ˈkroʊ.mə.soʊm/
Example:
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
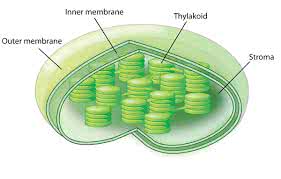
/ˈklɔːr.ə.plæst/
Example:
The plant cells are rich in chloroplasts, essential for photosynthesis.
/ˈsaɪ.t̬ə.plæz.əm/
Example:
Most of the cell's metabolic activities occur within the cytoplasm.
/ˈnuː.kli.oʊ/
Example:
Each strand of DNA is a long chain of nucleotides.
/ˈdʒiː.noʊm/
Example:
Scientists are working to map the human genome.
/ˌpɑː.liˈpep.taɪd/
Example:
The ribosome synthesizes a polypeptide chain.
/ˌɔːr.ɡənˈel/
Example:
Mitochondria are important organelles responsible for energy production.
/ˈvæk.ju.oʊl/
Example:
Plant cells often have a large central vacuole.
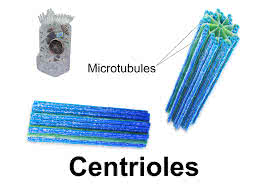
/ˈsen.tri.oʊl/
Example:
During cell division, the centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell.
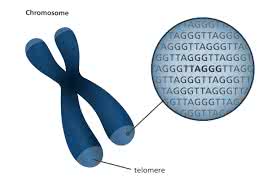
/ˈte.lə.mɪr/
Example:
The length of a telomere is often associated with cellular aging.
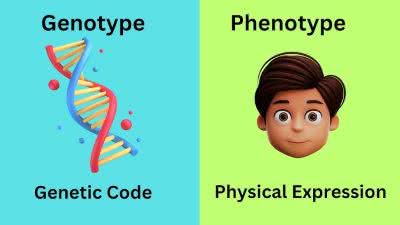
/ˈfiː.noʊ.taɪp/
Example:
The color of a flower is a clear phenotype.
/ˌhoʊ.mi.oʊˈsteɪ.sɪs/
Example:
The body maintains homeostasis through various regulatory mechanisms.
/trænsˈleɪ.ʃən/
Example:
The translation of the document took several hours.
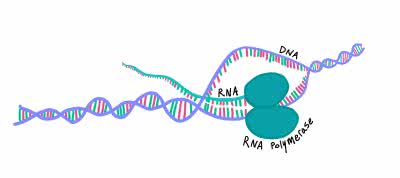
/trænˈskrɪp.ʃən/
Example:
The secretary provided a detailed transcription of the meeting minutes.
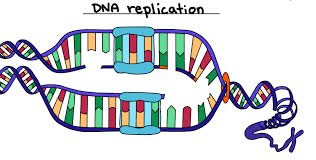
/ˌrep.ləˈkeɪ.ʃən/
Example:
The experiment requires careful replication to ensure accuracy.
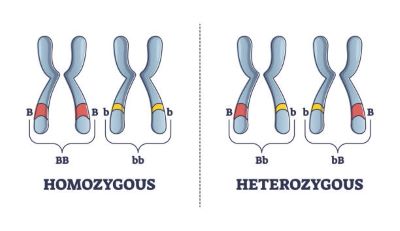
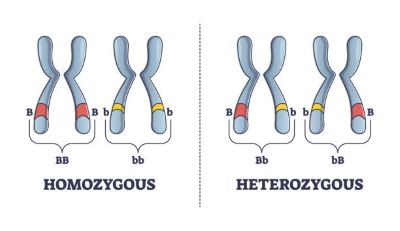
/ˌhet̬.ə.roʊˈzaɪ.ɡoʊt/
Example:
In this genetic cross, the heterozygote displays a phenotype intermediate between the two homozygotes.
/ˌhoʊ.məˈzaɪ.ɡoʊt/
Example:
The plant was a homozygote for the red flower gene.
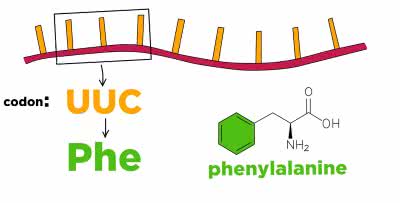
/ˈkoʊ.dɑːn/
Example:
Each codon specifies a particular amino acid.
/ˌsɪm.baɪˈoʊ.sɪs/
Example:
The clownfish and the sea anemone live in a perfect example of symbiosis.
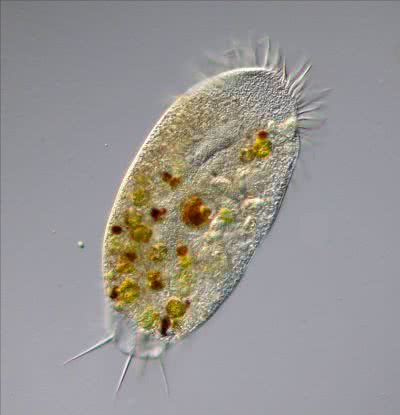
/əˈmiː.bə/
Example:
The ameba moved slowly across the microscope slide.
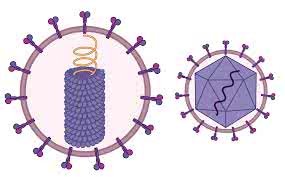
/ˈkæpsɪd/
Example:
The viral genome is protected by the capsid.
/ˈklɔːr.ə.fɪl/
Example:
The leaves get their green color from chlorophyll.
/juːˈker.i.oʊt/
Example:
Humans are eukaryotes, as our cells contain a nucleus.
/ˈfiː.t̬əs/
Example:
The doctor monitored the development of the fetus.
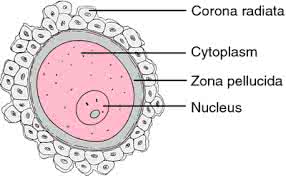
/ˈoʊ.vəm/
Example:
The fertilization of an ovum by a sperm marks the beginning of a new life.
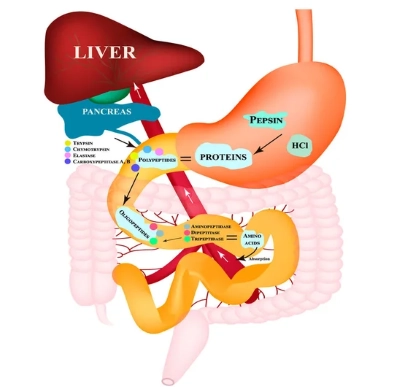
/ˈpep.sɪn/
Example:
Pepsin is crucial for the initial stages of protein digestion.
/proʊˈker.i.oʊt/
Example:
Bacteria are a common example of a prokaryote.