Nervous System Vocabulary Set in Body: Full and Detailed List
The 'Nervous System' vocabulary set in 'Body' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
Learn Now /ˈnʊr.ɑːn/
Example:
The brain contains billions of neurons.
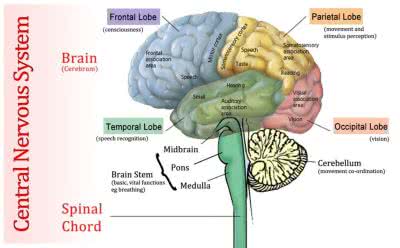
/breɪn/
Example:
The human brain is a complex organ.
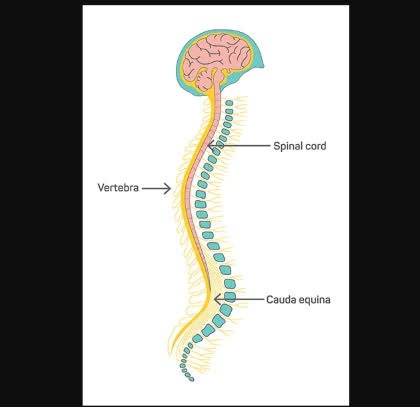
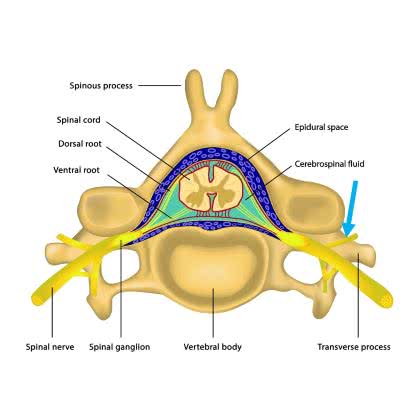
/ˈspaɪ.nəl ˌkɔːrd/
Example:
Damage to the spinal cord can result in paralysis.
/nɝːv/
Example:
The doctor tested his reflexes to check his nerves.
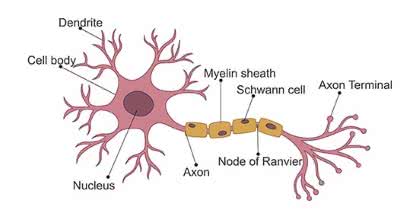
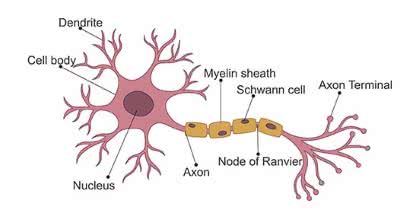
/ˈnɜːrv sel/
Example:
A nerve cell transmits electrical signals throughout the body.
/ˈsoʊ.lər ˈplek.səs/
Example:
He took a hard punch to the solar plexus and gasped for air.
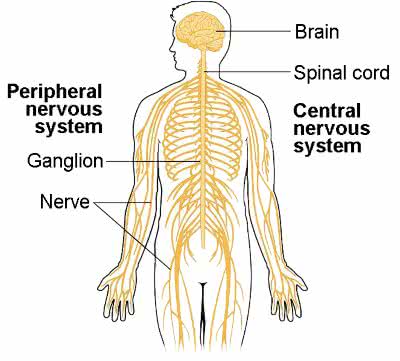
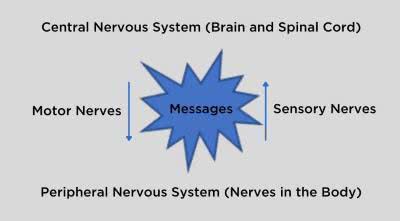
/ˈsen.trəl ˌnɜːr.vəs ˈsɪs.təm/
Example:
The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
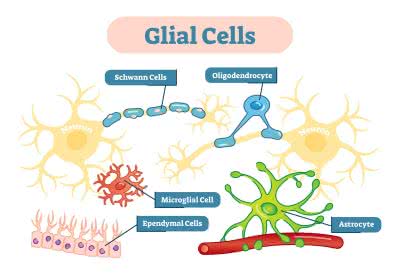
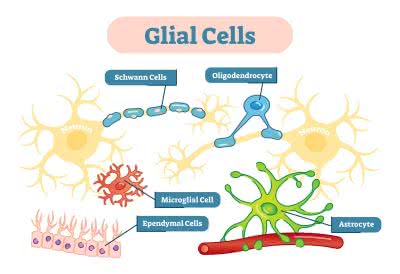
/ˈɡlaɪəl sel/
Example:
Glial cells play a crucial role in brain function by supporting neurons.
/ˈɡlaɪ.əl/
Example:
Glial cells play a crucial role in supporting neurons.
/pəˌrɪf.ər.əl ˈnɝː.vəs ˌsɪs.təm/
Example:
The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to the limbs and organs.
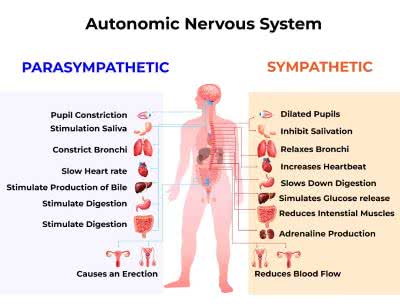
/ˌɔː.təˈnɑː.mɪk ˈnɝː.vəs ˌsɪs.təm/
Example:
The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions.
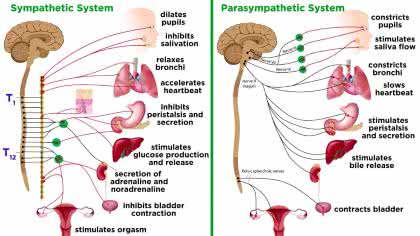
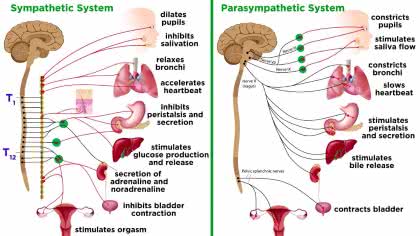
/ˌsɪm.pəˈθet.ɪk ˈnɜːr.vəs ˌsɪs.təm/
Example:
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the 'fight or flight' response.
parasympathetic nervous system
/ˌpærəˌsɪmpəˈθetɪk ˈnɜːrvəs ˌsɪstəm/
Example:
Activation of the parasympathetic nervous system promotes rest and digestion.
/soʊˈmætɪk ˈnɜːrvəs ˈsɪstəm/
Example:
The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements like walking and lifting.
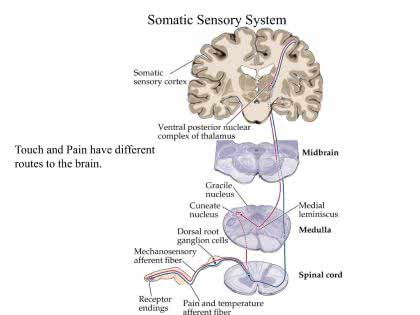
/soʊˈmætɪk ˈsɛnsəri ˈsɪstəm/
Example:
The somatic sensory system allows us to feel the texture of objects.
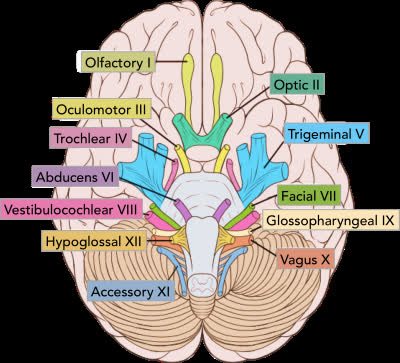
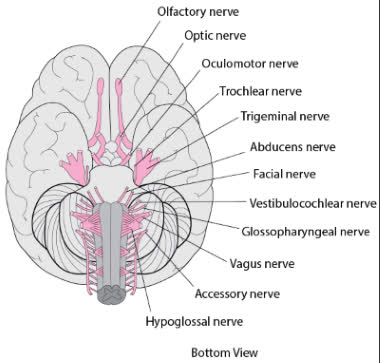
/ˈkreɪ.ni.əl nɜːrv/
Example:
The optic nerve is a cranial nerve responsible for vision.
/ˈspaɪ.nəl nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to a spinal nerve can result in loss of sensation or muscle weakness.
/ˈplek.səs/
Example:
The solar plexus is a complex network of nerves located in the abdomen.
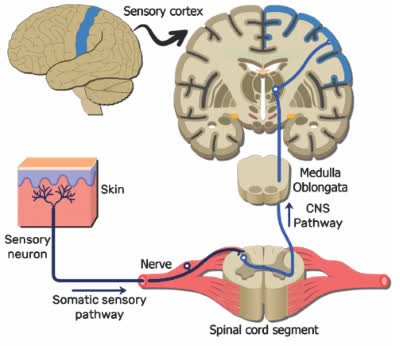
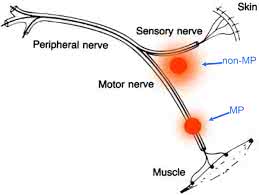
/ˈsen.sər.i ˌnɜːrv/
Example:
The sensory nerve transmits signals from the skin to the brain, allowing us to feel touch and temperature.
/ˈmoʊtər ˈnʊrɑn/
Example:
Damage to motor neurons can lead to muscle weakness and paralysis.
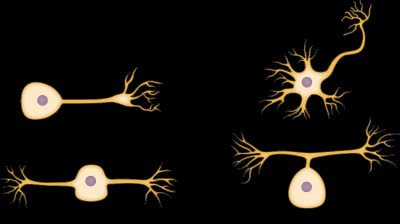
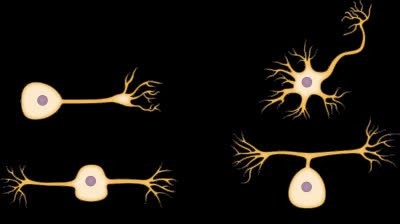
/ˌjuːnɪˈpoʊlər ˈnʊrɑːn/
Example:
Sensory neurons, such as those found in the dorsal root ganglia, are typically unipolar neurons.
/ˌmʌltɪˈpoʊlər ˈnʊrɑːn/
Example:
The majority of neurons in the brain are multipolar neurons, facilitating complex neural networks.
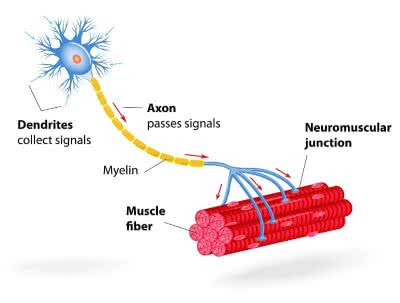
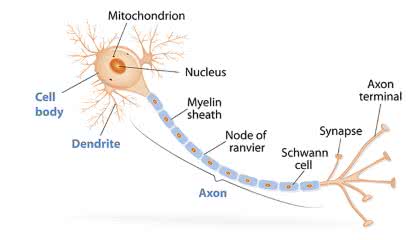
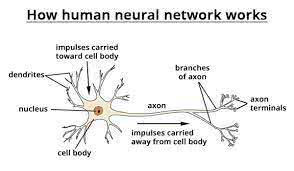
/ˈæk.sɑːn/
Example:
The electrical signal travels down the axon to the next neuron.
/ˈmoʊ.t̬ər ˌnɝːv/
Example:
The brain sends signals through the motor nerve to move your arm.
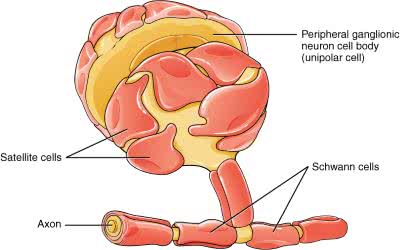
/ˈʃwɑːn sel/
Example:
Schwann cells are crucial for the regeneration of peripheral nerves.
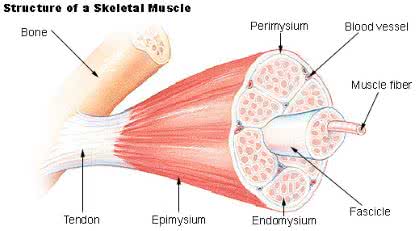
/ˈfæs.ɪ.kəl/
Example:
The nerve fascicle contains many individual nerve fibers.
/ˈfaɪ.bɚ/
Example:
Cotton fibers are used to make fabric.
/ˈɡæŋ.ɡli.ən/
Example:
The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons.
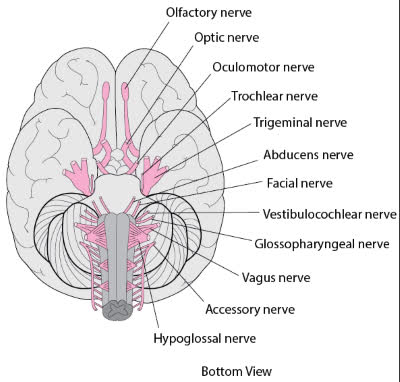
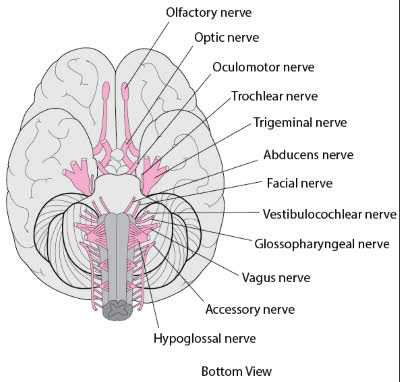
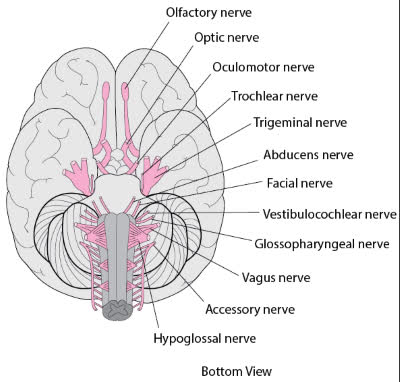
/oʊlˈfæktəri nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the olfactory nerve can result in a loss of the sense of smell.
/ˈɑːptɪk nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the optic nerve can lead to vision loss.
/ˌɑːk.jə.loʊˈmoʊ.t̬ər nɝːv/
Example:
Damage to the oculomotor nerve can lead to double vision and drooping eyelids.
/ˈtrɑːk.lɪər ˌnɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the trochlear nerve can lead to double vision.
/traɪˈdʒemɪnəl nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the trigeminal nerve can cause severe facial pain.
/æbˈduː.sənz nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the abducens nerve can result in double vision.
/ˈfeɪʃl nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the facial nerve can lead to Bell's palsy.
/ˌves.tɪ.bjə.loʊˈkɑːk.li.ər nɝːv/
Example:
Damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve can lead to hearing loss or balance problems.
/ˌɡlɑː.soʊ.fəˈrɪn.dʒi.əl nɝːv/
Example:
Damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve can affect swallowing and taste.
/ˈveɪ.ɡəs nɜːrv/
Example:
Stimulation of the vagus nerve can help regulate heart rate.
/əkˈsesəri nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the accessory nerve can lead to weakness in the shoulder and neck.
/ˌhaɪ.poʊˈɡlɑː.səl ˈnɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the hypoglossal nerve can lead to difficulties in speaking and eating.
/ˈnʊrəl ˈnetwɜːrk/
Example:
The company uses a neural network to detect fraud in financial transactions.
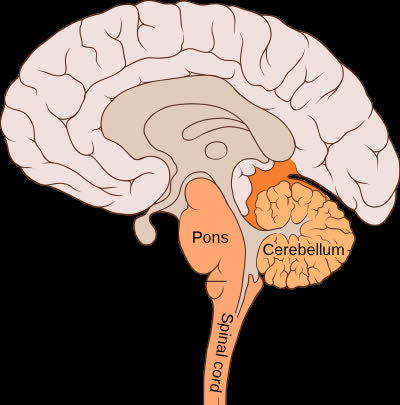
/pɑːnz/
Example:
The pons plays a crucial role in regulating sleep and respiration.
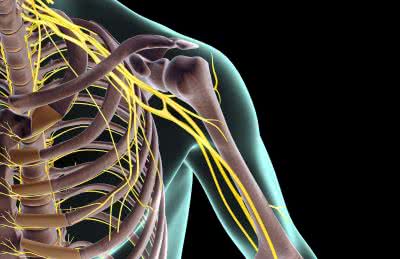
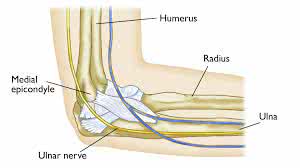
/ˈʌlnər nɜːrv/
Example:
Hitting your 'funny bone' actually means you've struck your ulnar nerve.
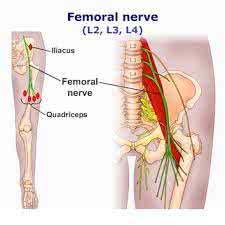
/ˈfem.ər.əl nɜːrv/
Example:
Damage to the femoral nerve can cause weakness in the leg.