Electrical English Terminology Vocabulary Set in Electricity Industry: Full and Detailed List
The 'Electrical English Terminology' vocabulary set in 'Electricity Industry' is carefully selected from standard international textbook sources, helping you master vocabulary in a short time. Comprehensive compilation of definitions, illustrative examples, and standard pronunciation...
Learn this vocabulary set on Lingoland
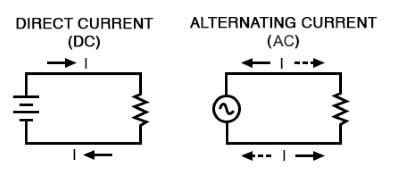
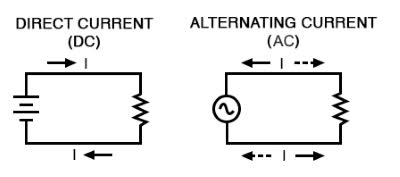
Learn Now /ˈɔːl.tərˌneɪ.tɪŋ ˈkɝː.ənt/
Example:
Most household appliances run on alternating current.
/ˌdɪ.rekt ˈkɝː.ənt/
Example:
Batteries produce direct current.
/wɑːt/
Example:
The light bulb uses 60 watts of power.
/ˈvoʊltˌmiː.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The technician used a voltmeter to check the battery's voltage.
/ˈæm.iː.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The electrician used an ammeter to check the circuit's current.
/əˈsɪl.ə.skoʊp/
Example:
The engineer used an oscilloscope to debug the circuit.
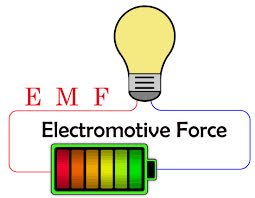
/ɪˌlɛktroʊˌmoʊtɪv ˈfɔːrs/
Example:
The battery provides the electromotive force for the circuit.
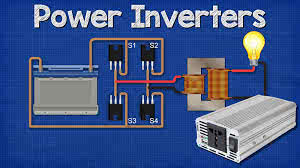
/ɪnˈvɝː.t̬ɚ/
Example:
The solar panels feed into an inverter to power the house.
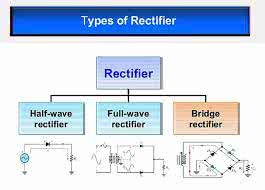
/ˈrek.tə.faɪ.ɚ/
Example:
The power supply uses a rectifier to convert AC to DC.
/ˈkɑːn.duː.ɪt/
Example:
The old pipes served as a conduit for wastewater.
/ˈfjuːz bɑːks/
Example:
I checked the fuse box, but all the fuses seemed fine.
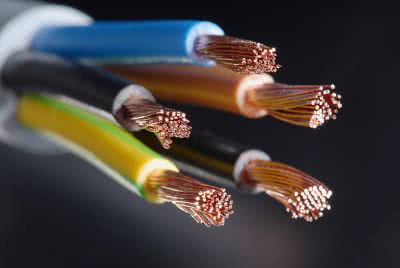
/ˈkeɪ.bəl/
Example:
The bridge is supported by strong steel cables.
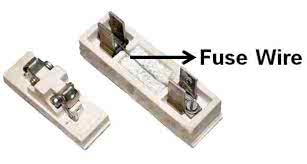
/fjuːz waɪər/
Example:
The electrician replaced the blown fuse wire.